iOS 如何实现 Aspect Oriented Programming
前言
在“Runtime病院”住院的后两天,分析了一下AOP的实现原理。“出院”后,发现Aspect库还没有详细分析,于是就有了这篇文章,今天就来说说iOS 是如何实现Aspect Oriented Programming。
目录
- 1.Aspect Oriented Programming简介
- 2.什么是Aspects
- 3.Aspects 中4个基本类 解析
- 4.Aspects hook前的准备工作
- 5.Aspects hook过程详解
- 6.关于Aspects的一些 “坑”
一.Aspect Oriented Programming简介
面向切面的程序设计(aspect-oriented programming,AOP,又译作面向方面的程序设计、观点导向编程、剖面导向程序设计)是计算机科学中的一个术语,指一种程序设计范型。该范型以一种称为侧面(aspect,又译作方面)的语言构造为基础,侧面是一种新的模块化机制,用来描述分散在对象、类或函数中的横切关注点(crosscutting concern)。
侧面的概念源于对面向对象的程序设计的改进,但并不只限于此,它还可以用来改进传统的函数。与侧面相关的编程概念还包括元对象协议、主题(subject)、混入(mixin)和委托。
AOP通过预编译方式和运行期动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术。
OOP(面向对象编程)针对业务处理过程的实体及其属性和行为进行抽象封装,以获得更加清晰高效的逻辑单元划分。
AOP则是针对业务处理过程中的切面进行提取,它所面对的是处理过程中的某个步骤或阶段,以获得逻辑过程中各部分之间低耦合性的隔离效果。
OOP和AOP属于两个不同的“思考方式”。OOP专注于对象的属性和行为的封装,AOP专注于处理某个步骤和阶段的,从中进行切面的提取。
举个例子,如果有一个判断权限的需求,OOP的做法肯定是在每个操作前都加入权限判断。那日志记录怎么办?在每个方法的开始结束的地方都加上日志记录。AOP就是把这些重复的逻辑和操作,提取出来,运用动态代理,实现这些模块的解耦。OOP和AOP不是互斥,而是相互配合。
在iOS里面使用AOP进行编程,可以实现非侵入。不需要更改之前的代码逻辑,就能加入新的功能。主要用来处理一些具有横切性质的系统性服务,如日志记录、权限管理、缓存、对象池管理等。
二. 什么是Aspects

Aspects是一个轻量级的面向切面编程的库。它能允许你在每一个类和每一个实例中存在的方法里面加入任何代码。可以在以下切入点插入代码:before(在原始的方法前执行) / instead(替换原始的方法执行) / after(在原始的方法后执行,默认)。通过Runtime消息转发实现Hook。Aspects会自动的调用super方法,使用method swizzling起来会更加方便。
这个库很稳定,目前用在数百款app上了。它也是PSPDFKit的一部分,PSPDFKit是一个iOS 看PDF的framework库。作者最终决定把它开源出来。
三.Aspects 中4个基本类 解析
我们从头文件开始看起。
1.Aspects.h
typedef NS_OPTIONS(NSUInteger, AspectOptions) {
AspectPositionAfter = 0, /// Called after the original implementation (default)
AspectPositionInstead = 1, /// Will replace the original implementation.
AspectPositionBefore = 2, /// Called before the original implementation.
AspectOptionAutomaticRemoval = 1 << 3 /// Will remove the hook after the first execution.
};
在头文件中定义了一个枚举。这个枚举里面是调用切片方法的时机。默认是AspectPositionAfter在原方法执行完之后调用。AspectPositionInstead是替换原方法。AspectPositionBefore是在原方法之前调用切片方法。AspectOptionAutomaticRemoval是在hook执行完自动移除。
@protocol AspectToken <NSObject>
- (BOOL)remove;
@end
定义了一个AspectToken的协议,这里的Aspect Token是隐式的,允许我们调用remove去撤销一个hook。remove方法返回YES代表撤销成功,返回NO就撤销失败。
@protocol AspectInfo <NSObject>
- (id)instance;
- (NSInvocation *)originalInvocation;
- (NSArray *)arguments;
@end
又定义了一个AspectInfo协议。AspectInfo protocol是我们block语法里面的第一个参数。
instance方法返回当前被hook的实例。originalInvocation方法返回被hooked方法的原始的invocation。arguments方法返回所有方法的参数。它的实现是懒加载。
头文件中还特意给了一段注释来说明Aspects的用法和注意点,值得我们关注。
/**
Aspects uses Objective-C message forwarding to hook into messages. This will create some overhead. Don't add aspects to methods that are called a lot. Aspects is meant for view/controller code that is not called a 1000 times per second.
Adding aspects returns an opaque token which can be used to deregister again. All calls are thread safe.
*/
Aspects利用的OC的消息转发机制,hook消息。这样会有一些性能开销。不要把Aspects加到经常被使用的方法里面。Aspects是用来设计给view/controller 代码使用的,而不是用来hook每秒调用1000次的方法的。
添加Aspects之后,会返回一个隐式的token,这个token会被用来注销hook方法的。所有的调用都是线程安全的。
关于线程安全,下面会详细分析。现在至少我们知道Aspects不应该被用在for循环这些方法里面,会造成很大的性能损耗。
@interface NSObject (Aspects)
/// Adds a block of code before/instead/after the current `selector` for a specific class.
///
/// @param block Aspects replicates the type signature of the method being hooked.
/// The first parameter will be `id<AspectInfo>`, followed by all parameters of the method.
/// These parameters are optional and will be filled to match the block signature.
/// You can even use an empty block, or one that simple gets `id<AspectInfo>`.
///
/// @note Hooking static methods is not supported.
/// @return A token which allows to later deregister the aspect.
+ (id<AspectToken>)aspect_hookSelector:(SEL)selector
withOptions:(AspectOptions)options
usingBlock:(id)block
error:(NSError **)error;
/// Adds a block of code before/instead/after the current `selector` for a specific instance.
- (id<AspectToken>)aspect_hookSelector:(SEL)selector
withOptions:(AspectOptions)options
usingBlock:(id)block
error:(NSError **)error;
@end
Aspects整个库里面就只有这两个方法。这里可以看到,Aspects是NSobject的一个extension,只要是NSObject,都可以使用这两个方法。这两个方法名字都是同一个,入参和返回值也一样,唯一不同的是一个是加号方法一个是减号方法。一个是用来hook类方法,一个是用来hook实例方法。
方法里面有4个入参。第一个selector是要给它增加切面的原方法。第二个参数是AspectOptions类型,是代表这个切片增加在原方法的before / instead / after。第4个参数是返回的错误。
重点的就是第三个入参block。这个block复制了正在被hook的方法的签名signature类型。block遵循AspectInfo协议。我们甚至可以使用一个空的block。AspectInfo协议里面的参数是可选的,主要是用来匹配block签名的。
返回值是一个token,可以被用来注销这个Aspects。
注意,Aspects是不支持hook 静态static方法的
typedef NS_ENUM(NSUInteger, AspectErrorCode) {
AspectErrorSelectorBlacklisted, /// Selectors like release, retain, autorelease are blacklisted.
AspectErrorDoesNotRespondToSelector, /// Selector could not be found.
AspectErrorSelectorDeallocPosition, /// When hooking dealloc, only AspectPositionBefore is allowed.
AspectErrorSelectorAlreadyHookedInClassHierarchy, /// Statically hooking the same method in subclasses is not allowed.
AspectErrorFailedToAllocateClassPair, /// The runtime failed creating a class pair.
AspectErrorMissingBlockSignature, /// The block misses compile time signature info and can't be called.
AspectErrorIncompatibleBlockSignature, /// The block signature does not match the method or is too large.
AspectErrorRemoveObjectAlreadyDeallocated = 100 /// (for removing) The object hooked is already deallocated.
};
extern NSString *const AspectErrorDomain;
这里定义了错误码的类型。出错的时候方便我们调试。
2.Aspects.m
#import "Aspects.h"
#import <libkern/OSAtomic.h>
#import <objc/runtime.h>
#import <objc/message.h>
#import <libkern/OSAtomic.h>导入这个头文件是为了下面用到的自旋锁。#import <objc/runtime.h> 和 #import <objc/message.h>是使用Runtime的必备头文件。
typedef NS_OPTIONS(int, AspectBlockFlags) {
AspectBlockFlagsHasCopyDisposeHelpers = (1 << 25),
AspectBlockFlagsHasSignature = (1 << 30)
};
定义了AspectBlockFlags,这是一个flag,用来标记两种情况,是否需要Copy和Dispose的Helpers,是否需要方法签名Signature 。
在Aspects中定义的4个类,分别是AspectInfo,AspectIdentifier,AspectsContainer,AspectTracker。接下来就分别看看这4个类是怎么定义的。
3. AspectInfo
@interface AspectInfo : NSObject <AspectInfo>
- (id)initWithInstance:(__unsafe_unretained id)instance invocation:(NSInvocation *)invocation;
@property (nonatomic, unsafe_unretained, readonly) id instance;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSArray *arguments;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSInvocation *originalInvocation;
@end
AspectInfo对应的实现
#pragma mark - AspectInfo
@implementation AspectInfo
@synthesize arguments = _arguments;
- (id)initWithInstance:(__unsafe_unretained id)instance invocation:(NSInvocation *)invocation {
NSCParameterAssert(instance);
NSCParameterAssert(invocation);
if (self = [super init]) {
_instance = instance;
_originalInvocation = invocation;
}
return self;
}
- (NSArray *)arguments {
// Lazily evaluate arguments, boxing is expensive.
if (!_arguments) {
_arguments = self.originalInvocation.aspects_arguments;
}
return _arguments;
}
AspectInfo是继承于NSObject,并且遵循了AspectInfo协议。在其 - (id)initWithInstance: invocation:方法中,把外面传进来的实例instance,和原始的invocation保存到AspectInfo类对应的成员变量中。- (NSArray *)arguments方法是一个懒加载,返回的是原始的invocation里面的aspects参数数组。
aspects_arguments这个getter方法是怎么实现的呢?作者是通过一个为NSInvocation添加一个分类来实现的。
@interface NSInvocation (Aspects)
- (NSArray *)aspects_arguments;
@end
为原始的NSInvocation类添加一个Aspects分类,这个分类中只增加一个方法,aspects_arguments,返回值是一个数组,数组里面包含了当前invocation的所有参数。
对应的实现
#pragma mark - NSInvocation (Aspects)
@implementation NSInvocation (Aspects)
- (NSArray *)aspects_arguments {
NSMutableArray *argumentsArray = [NSMutableArray array];
for (NSUInteger idx = 2; idx < self.methodSignature.numberOfArguments; idx++) {
[argumentsArray addObject:[self aspect_argumentAtIndex:idx] ?: NSNull.null];
}
return [argumentsArray copy];
}
@end
- (NSArray *)aspects_arguments实现很简单,就是一层for循环,把methodSignature方法签名里面的参数,都加入到数组里,最后把数组返回。
关于获取方法所有参数的这个- (NSArray *)aspects_arguments方法的实现,有2个地方需要详细说明。一是为什么循环从2开始,二是[self aspect_argumentAtIndex:idx]内部是怎么实现的。

先来说说为啥循环从2开始。
Type Encodings作为对Runtime的补充,编译器将每个方法的返回值和参数类型编码为一个字符串,并将其与方法的selector关联在一起。这种编码方案在其它情况下也是非常有用的,因此我们可以使用@encode编译器指令来获取它。当给定一个类型时,@encode返回这个类型的字符串编码。这些类型可以是诸如int、指针这样的基本类型,也可以是结构体、类等类型。事实上,任何可以作为sizeof()操作参数的类型都可以用于@encode()。
在Objective-C Runtime Programming Guide中的Type Encoding一节中,列出了Objective-C中所有的类型编码。需要注意的是这些类型很多是与我们用于存档和分发的编码类型是相同的。但有一些不能在存档时使用。
注:Objective-C不支持long double类型。@encode(long double)返回d,与double是一样的。

OC为支持消息的转发和动态调用,Objective-C Method 的 Type 信息以 “返回值 Type + 参数 Types” 的形式组合编码,还需要考虑到 self 和 _cmd 这两个隐含参数:
- (void)tap; => "v@:"
- (int)tapWithView:(double)pointx; => "i@:d"
按照上面的表,我们可以知道,编码出来的字符串,前3位分别是返回值Type,self隐含参数Type @,_cmd隐含参数Type :。
所以从第3位开始,是入参。
假设我们以- (void)tapView:(UIView *)view atIndex:(NSInteger)index为例,打印一下methodSignature
(lldb) po self.methodSignature
<NSMethodSignature: 0x60800007df00>
number of arguments = 4
frame size = 224
is special struct return? NO
return value: -------- -------- -------- --------
type encoding (v) 'v'
flags {}
modifiers {}
frame {offset = 0, offset adjust = 0, size = 0, size adjust = 0}
memory {offset = 0, size = 0}
argument 0: -------- -------- -------- --------
type encoding (@) '@'
flags {isObject}
modifiers {}
frame {offset = 0, offset adjust = 0, size = 8, size adjust = 0}
memory {offset = 0, size = 8}
argument 1: -------- -------- -------- --------
type encoding (:) ':'
flags {}
modifiers {}
frame {offset = 8, offset adjust = 0, size = 8, size adjust = 0}
memory {offset = 0, size = 8}
argument 2: -------- -------- -------- --------
type encoding (@) '@'
flags {isObject}
modifiers {}
frame {offset = 16, offset adjust = 0, size = 8, size adjust = 0}
memory {offset = 0, size = 8}
argument 3: -------- -------- -------- --------
type encoding (q) 'q'
flags {isSigned}
modifiers {}
frame {offset = 24, offset adjust = 0, size = 8, size adjust = 0}
memory {offset = 0, size = 8}
number of arguments = 4,因为有2个隐含参数self和_cmd,加上入参view和index。

第一个argument的frame {offset = 0, offset adjust = 0, size = 0, size adjust = 0}memory {offset = 0, size = 0},返回值在这里不占size。第二个argument是self,frame {offset = 0, offset adjust = 0, size = 8, size adjust = 0}memory {offset = 0, size = 8}。由于size = 8,下一个frame的offset就是8,之后是16,以此类推。
至于为何这里要传递2,还跟aspect_argumentAtIndex具体实现有关系。
再来看看aspect_argumentAtIndex的具体实现。这个方法还要感谢ReactiveCocoa团队,为获取方法签名的参数提供了一种优雅的实现方式。
// Thanks to the ReactiveCocoa team for providing a generic solution for this.
- (id)aspect_argumentAtIndex:(NSUInteger)index {
const char *argType = [self.methodSignature getArgumentTypeAtIndex:index];
// Skip const type qualifier.
if (argType[0] == _C_CONST) argType++;
#define WRAP_AND_RETURN(type) do { type val = 0; [self getArgument:&val atIndex:(NSInteger)index]; return @(val); } while (0)
if (strcmp(argType, @encode(id)) == 0 || strcmp(argType, @encode(Class)) == 0) {
__autoreleasing id returnObj;
[self getArgument:&returnObj atIndex:(NSInteger)index];
return returnObj;
} else if (strcmp(argType, @encode(SEL)) == 0) {
SEL selector = 0;
[self getArgument:&selector atIndex:(NSInteger)index];
return NSStringFromSelector(selector);
} else if (strcmp(argType, @encode(Class)) == 0) {
__autoreleasing Class theClass = Nil;
[self getArgument:&theClass atIndex:(NSInteger)index];
return theClass;
// Using this list will box the number with the appropriate constructor, instead of the generic NSValue.
} else if (strcmp(argType, @encode(char)) == 0) {
WRAP_AND_RETURN(char);
} else if (strcmp(argType, @encode(int)) == 0) {
WRAP_AND_RETURN(int);
} else if (strcmp(argType, @encode(short)) == 0) {
WRAP_AND_RETURN(short);
} else if (strcmp(argType, @encode(long)) == 0) {
WRAP_AND_RETURN(long);
} else if (strcmp(argType, @encode(long long)) == 0) {
WRAP_AND_RETURN(long long);
} else if (strcmp(argType, @encode(unsigned char)) == 0) {
WRAP_AND_RETURN(unsigned char);
} else if (strcmp(argType, @encode(unsigned int)) == 0) {
WRAP_AND_RETURN(unsigned int);
} else if (strcmp(argType, @encode(unsigned short)) == 0) {
WRAP_AND_RETURN(unsigned short);
} else if (strcmp(argType, @encode(unsigned long)) == 0) {
WRAP_AND_RETURN(unsigned long);
} else if (strcmp(argType, @encode(unsigned long long)) == 0) {
WRAP_AND_RETURN(unsigned long long);
} else if (strcmp(argType, @encode(float)) == 0) {
WRAP_AND_RETURN(float);
} else if (strcmp(argType, @encode(double)) == 0) {
WRAP_AND_RETURN(double);
} else if (strcmp(argType, @encode(BOOL)) == 0) {
WRAP_AND_RETURN(BOOL);
} else if (strcmp(argType, @encode(bool)) == 0) {
WRAP_AND_RETURN(BOOL);
} else if (strcmp(argType, @encode(char *)) == 0) {
WRAP_AND_RETURN(const char *);
} else if (strcmp(argType, @encode(void (^)(void))) == 0) {
__unsafe_unretained id block = nil;
[self getArgument:&block atIndex:(NSInteger)index];
return [block copy];
} else {
NSUInteger valueSize = 0;
NSGetSizeAndAlignment(argType, &valueSize, NULL);
unsigned char valueBytes[valueSize];
[self getArgument:valueBytes atIndex:(NSInteger)index];
return [NSValue valueWithBytes:valueBytes objCType:argType];
}
return nil;
#undef WRAP_AND_RETURN
}
getArgumentTypeAtIndex:这个方法是用来获取到methodSignature方法签名指定index的type encoding的字符串。这个方法传出来的字符串直接就是我们传进去的index值。比如我们传进去的是2,其实传出来的字符串是methodSignature对应的字符串的第3位。
由于第0位是函数返回值return value对应的type encoding,所以传进来的2,对应的是argument2。所以我们这里传递index = 2进来,就是过滤掉了前3个type encoding的字符串,从argument2开始比较。这就是为何循环从2开始的原因。

_C_CONST是一个常量,用来判断encoding的字符串是不是CONST常量。
#define _C_ID '@'
#define _C_CLASS '#'
#define _C_SEL ':'
#define _C_CHR 'c'
#define _C_UCHR 'C'
#define _C_SHT 's'
#define _C_USHT 'S'
#define _C_INT 'i'
#define _C_UINT 'I'
#define _C_LNG 'l'
#define _C_ULNG 'L'
#define _C_LNG_LNG 'q'
#define _C_ULNG_LNG 'Q'
#define _C_FLT 'f'
#define _C_DBL 'd'
#define _C_BFLD 'b'
#define _C_BOOL 'B'
#define _C_VOID 'v'
#define _C_UNDEF '?'
#define _C_PTR '^'
#define _C_CHARPTR '*'
#define _C_ATOM '%'
#define _C_ARY_B '['
#define _C_ARY_E ']'
#define _C_UNION_B '('
#define _C_UNION_E ')'
#define _C_STRUCT_B '{'
#define _C_STRUCT_E '}'
#define _C_VECTOR '!'
#define _C_CONST 'r'
这里的Type和OC的Type 是完全一样的,只不过这里是一个C的char类型。
#define WRAP_AND_RETURN(type) do { type val = 0; [self getArgument:&val atIndex:(NSInteger)index]; return @(val); } while (0)
WRAP_AND_RETURN是一个宏定义。这个宏定义里面调用的getArgument:atIndex:方法是用来在NSInvocation中根据index得到对应的Argument,最后return的时候把val包装成对象,返回出去。
在下面大段的if - else判断中,有很多字符串比较的函数strcmp。
比如说strcmp(argType, @encode(id)) == 0,argType是一个char,内容是methodSignature取出来对应的type encoding,和@encode(id)是一样的type encoding。通过strcmp比较之后,如果是0,代表类型是相同的。
下面的大段的判断就是把入参都返回的过程,依次判断了id,class,SEL,接着是一大推基本类型,char,int,short,long,long long,unsigned char,unsigned int,unsigned short,unsigned long,unsigned long long,float,double,BOOL,bool,char *这些基本类型都会利用WRAP_AND_RETURN打包成对象返回。最后判断block和struct结构体,也会返回对应的对象。
这样入参就都返回到数组里面被接收了。假设还是上面- (void)tapView:(UIView *)view atIndex:(NSInteger)index为例子,执行完aspects_arguments,数组里面装的的是:
(
<UIView: 0x7fa2e2504190; frame = (0 80; 414 40); layer = <CALayer: 0x6080000347c0>>",
1
)
总结,AspectInfo里面主要是 NSInvocation 信息。将NSInvocation包装一层,比如参数信息等。
4. AspectIdentifier

// Tracks a single aspect.
@interface AspectIdentifier : NSObject
+ (instancetype)identifierWithSelector:(SEL)selector object:(id)object options:(AspectOptions)options block:(id)block error:(NSError **)error;
- (BOOL)invokeWithInfo:(id<AspectInfo>)info;
@property (nonatomic, assign) SEL selector;
@property (nonatomic, strong) id block;
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSMethodSignature *blockSignature;
@property (nonatomic, weak) id object;
@property (nonatomic, assign) AspectOptions options;
@end
对应实现
#pragma mark - AspectIdentifier
@implementation AspectIdentifier
+ (instancetype)identifierWithSelector:(SEL)selector object:(id)object options:(AspectOptions)options block:(id)block error:(NSError **)error {
NSCParameterAssert(block);
NSCParameterAssert(selector);
NSMethodSignature *blockSignature = aspect_blockMethodSignature(block, error); // TODO: check signature compatibility, etc.
if (!aspect_isCompatibleBlockSignature(blockSignature, object, selector, error)) {
return nil;
}
AspectIdentifier *identifier = nil;
if (blockSignature) {
identifier = [AspectIdentifier new];
identifier.selector = selector;
identifier.block = block;
identifier.blockSignature = blockSignature;
identifier.options = options;
identifier.object = object; // weak
}
return identifier;
}
- (BOOL)invokeWithInfo:(id<AspectInfo>)info {
NSInvocation *blockInvocation = [NSInvocation invocationWithMethodSignature:self.blockSignature];
NSInvocation *originalInvocation = info.originalInvocation;
NSUInteger numberOfArguments = self.blockSignature.numberOfArguments;
// Be extra paranoid. We already check that on hook registration.
if (numberOfArguments > originalInvocation.methodSignature.numberOfArguments) {
AspectLogError(@"Block has too many arguments. Not calling %@", info);
return NO;
}
// The `self` of the block will be the AspectInfo. Optional.
if (numberOfArguments > 1) {
[blockInvocation setArgument:&info atIndex:1];
}
void *argBuf = NULL;
for (NSUInteger idx = 2; idx < numberOfArguments; idx++) {
const char *type = [originalInvocation.methodSignature getArgumentTypeAtIndex:idx];
NSUInteger argSize;
NSGetSizeAndAlignment(type, &argSize, NULL);
if (!(argBuf = reallocf(argBuf, argSize))) {
AspectLogError(@"Failed to allocate memory for block invocation.");
return NO;
}
[originalInvocation getArgument:argBuf atIndex:idx];
[blockInvocation setArgument:argBuf atIndex:idx];
}
[blockInvocation invokeWithTarget:self.block];
if (argBuf != NULL) {
free(argBuf);
}
return YES;
}
- (NSString *)description {
return [NSString stringWithFormat:@"<%@: %p, SEL:%@ object:%@ options:%tu block:%@ (#%tu args)>", self.class, self, NSStringFromSelector(self.selector), self.object, self.options, self.block, self.blockSignature.numberOfArguments];
}
- (BOOL)remove {
return aspect_remove(self, NULL);
}
@end
在instancetype方法中调用了aspect_blockMethodSignature方法。
static NSMethodSignature *aspect_blockMethodSignature(id block, NSError **error) {
AspectBlockRef layout = (__bridge void *)block;
if (!(layout->flags & AspectBlockFlagsHasSignature)) {
NSString *description = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"The block %@ doesn't contain a type signature.", block];
AspectError(AspectErrorMissingBlockSignature, description);
return nil;
}
void *desc = layout->descriptor;
desc += 2 * sizeof(unsigned long int);
if (layout->flags & AspectBlockFlagsHasCopyDisposeHelpers) {
desc += 2 * sizeof(void *);
}
if (!desc) {
NSString *description = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"The block %@ doesn't has a type signature.", block];
AspectError(AspectErrorMissingBlockSignature, description);
return nil;
}
const char *signature = (*(const char **)desc);
return [NSMethodSignature signatureWithObjCTypes:signature];
}
这个aspect_blockMethodSignature的目的是把传递进来的AspectBlock转换成NSMethodSignature的方法签名。
AspectBlock的结构如下
typedef struct _AspectBlock {
__unused Class isa;
AspectBlockFlags flags;
__unused int reserved;
void (__unused *invoke)(struct _AspectBlock *block, ...);
struct {
unsigned long int reserved;
unsigned long int size;
// requires AspectBlockFlagsHasCopyDisposeHelpers
void (*copy)(void *dst, const void *src);
void (*dispose)(const void *);
// requires AspectBlockFlagsHasSignature
const char *signature;
const char *layout;
} *descriptor;
// imported variables
} *AspectBlockRef;
这里定义了一个Aspects内部使用的block类型。对系统的Block很熟悉的同学一眼就会感觉两者很像。不熟悉的可以看看我之前分析Block的文章。文章里,用Clang把Block转换成结构体,结构和这里定义的block很相似。
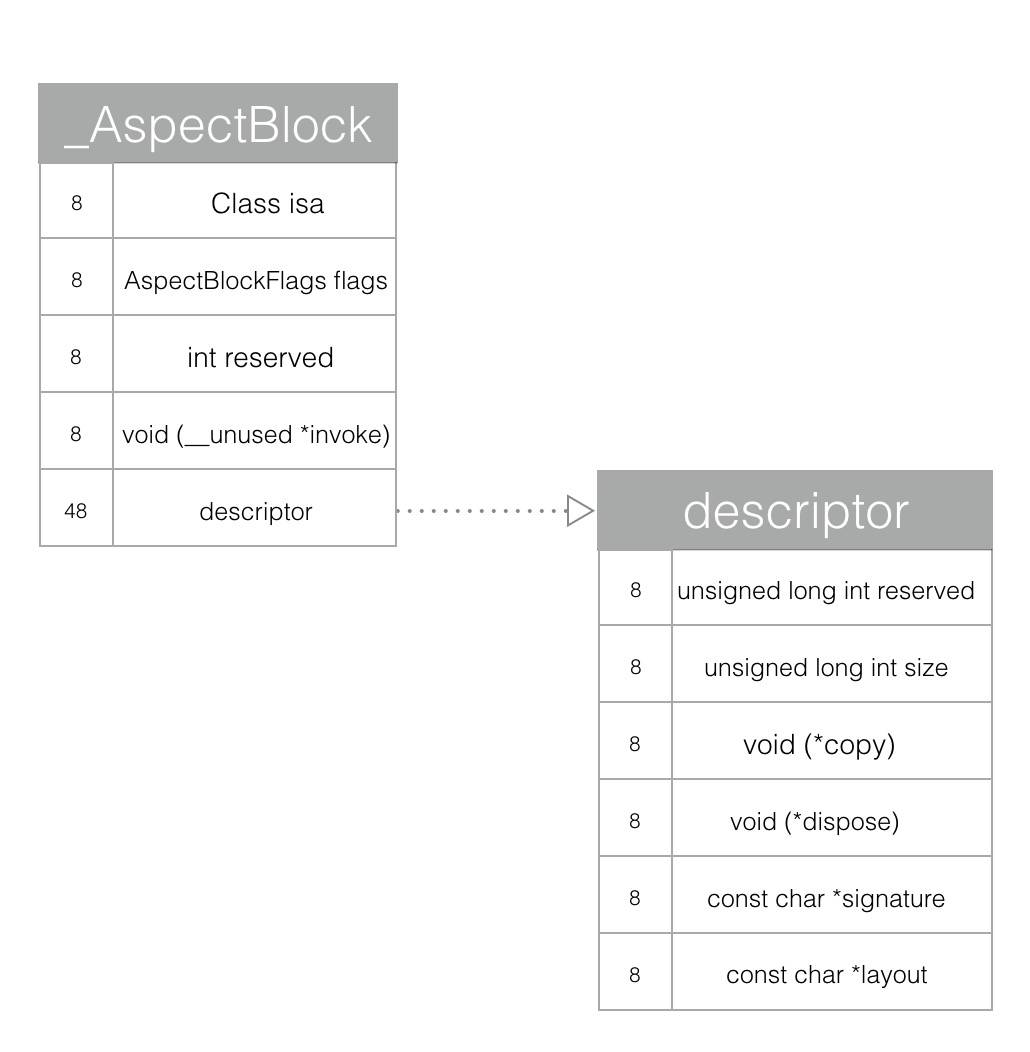
了解了AspectBlock的结构之后,再看aspect_blockMethodSignature函数就比较清楚了。
AspectBlockRef layout = (__bridge void *)block;
if (!(layout->flags & AspectBlockFlagsHasSignature)) {
NSString *description = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"The block %@ doesn't contain a type signature.", block];
AspectError(AspectErrorMissingBlockSignature, description);
return nil;
}
AspectBlockRef layout = (__bridge void *)block,由于两者block实现类似,所以这里先把入参block强制转换成AspectBlockRef类型,然后判断是否有AspectBlockFlagsHasSignature的标志位,如果没有,报不包含方法签名的error。
注意,传入的block是全局类型的
(__NSGlobalBlock) __NSGlobalBlock = {
NSBlock = {
NSObject = {
isa = __NSGlobalBlock__
}
}
}
void *desc = layout->descriptor;
desc += 2 * sizeof(unsigned long int);
if (layout->flags & AspectBlockFlagsHasCopyDisposeHelpers) {
desc += 2 * sizeof(void *);
}
if (!desc) {
NSString *description = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"The block %@ doesn't has a type signature.", block];
AspectError(AspectErrorMissingBlockSignature, description);
return nil;
}
desc就是原来block里面对应的descriptor指针。descriptor指针往下偏移2个unsigned long int的位置就指向了copy函数的地址,如果包含Copy和Dispose函数,那么继续往下偏移2个(void *)的大小。这时指针肯定移动到了const char *signature的位置。如果desc不存在,那么也会报错,该block不包含方法签名。
const char *signature = (*(const char **)desc);
return [NSMethodSignature signatureWithObjCTypes:signature];
到了这里,就保证有方法签名,且存在。最后调用NSMethodSignature的signatureWithObjCTypes方法,返回方法签名。
举例说明aspect_blockMethodSignature最终生成的方法签名是什么样子的。
[UIView aspect_hookSelector:@selector(UIView:atIndex:) withOptions:AspectPositionAfter usingBlock:^(id<AspectInfo> aspects, UIView *view, NSInteger index)
{
NSLog(@"按钮点击了 %ld",index);
} error:nil];
const char *signature最终获得的字符串是这样
(const char *) signature = 0x0000000102f72676 "v32@?0@\"<AspectInfo>\"8@\"UIView\"16q24"
v32@?0@“"8@“UIView"16q24是Block
^(id<AspectInfo> aspects, UIView *view, NSInteger index){
}
对应的Type。void返回值的Type是v,32是offset,@?是block对应的Type,@“”是第一个参数,@“UIView"是第二个参数,NSInteger对应的Type就是q了。
每个Type后面跟的数字都是它们各自对应的offset。把最终转换好的NSMethodSignature打印出来。
<NSMethodSignature: 0x600000263dc0>
number of arguments = 4
frame size = 224
is special struct return? NO
return value: -------- -------- -------- --------
type encoding (v) 'v'
flags {}
modifiers {}
frame {offset = 0, offset adjust = 0, size = 0, size adjust = 0}
memory {offset = 0, size = 0}
argument 0: -------- -------- -------- --------
type encoding (@) '@?'
flags {isObject, isBlock}
modifiers {}
frame {offset = 0, offset adjust = 0, size = 8, size adjust = 0}
memory {offset = 0, size = 8}
argument 1: -------- -------- -------- --------
type encoding (@) '@"<AspectInfo>"'
flags {isObject}
modifiers {}
frame {offset = 8, offset adjust = 0, size = 8, size adjust = 0}
memory {offset = 0, size = 8}
conforms to protocol 'AspectInfo'
argument 2: -------- -------- -------- --------
type encoding (@) '@"UIView"'
flags {isObject}
modifiers {}
frame {offset = 16, offset adjust = 0, size = 8, size adjust = 0}
memory {offset = 0, size = 8}
class 'DLMenuView'
argument 3: -------- -------- -------- --------
type encoding (q) 'q'
flags {isSigned}
modifiers {}
frame {offset = 24, offset adjust = 0, size = 8, size adjust = 0}
memory {offset = 0, size = 8}
回到AspectIdentifier中继续看instancetype方法,获取到了传入的block的方法签名之后,又调用了aspect_isCompatibleBlockSignature方法。
static BOOL aspect_isCompatibleBlockSignature(NSMethodSignature *blockSignature, id object, SEL selector, NSError **error) {
NSCParameterAssert(blockSignature);
NSCParameterAssert(object);
NSCParameterAssert(selector);
BOOL signaturesMatch = YES;
NSMethodSignature *methodSignature = [[object class] instanceMethodSignatureForSelector:selector];
if (blockSignature.numberOfArguments > methodSignature.numberOfArguments) {
signaturesMatch = NO;
}else {
if (blockSignature.numberOfArguments > 1) {
const char *blockType = [blockSignature getArgumentTypeAtIndex:1];
if (blockType[0] != '@') {
signaturesMatch = NO;
}
}
// Argument 0 is self/block, argument 1 is SEL or id<AspectInfo>. We start comparing at argument 2.
// The block can have less arguments than the method, that's ok.
if (signaturesMatch) {
for (NSUInteger idx = 2; idx < blockSignature.numberOfArguments; idx++) {
const char *methodType = [methodSignature getArgumentTypeAtIndex:idx];
const char *blockType = [blockSignature getArgumentTypeAtIndex:idx];
// Only compare parameter, not the optional type data.
if (!methodType || !blockType || methodType[0] != blockType[0]) {
signaturesMatch = NO; break;
}
}
}
}
if (!signaturesMatch) {
NSString *description = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"Block signature %@ doesn't match %@.", blockSignature, methodSignature];
AspectError(AspectErrorIncompatibleBlockSignature, description);
return NO;
}
return YES;
}
这个函数的作用是把我们要替换的方法block和要替换的原方法,进行对比。如何对比呢?对比两者的方法签名。
入参selector是原方法。
if (blockSignature.numberOfArguments > methodSignature.numberOfArguments) {
signaturesMatch = NO;
}else {
if (blockSignature.numberOfArguments > 1) {
const char *blockType = [blockSignature getArgumentTypeAtIndex:1];
if (blockType[0] != '@') {
signaturesMatch = NO;
}
}
先比较方法签名的参数个数是否相等,不等肯定是不匹配,signaturesMatch = NO。如果参数个数相等,再比较我们要替换的方法里面第一个参数是不是_cmd,对应的Type就是@,如果不是,也是不匹配,所以signaturesMatch = NO。如果上面两条都满足,signaturesMatch = YES,那么就进入下面更加严格的对比。
if (signaturesMatch) {
for (NSUInteger idx = 2; idx < blockSignature.numberOfArguments; idx++) {
const char *methodType = [methodSignature getArgumentTypeAtIndex:idx];
const char *blockType = [blockSignature getArgumentTypeAtIndex:idx];
// Only compare parameter, not the optional type data.
if (!methodType || !blockType || methodType[0] != blockType[0]) {
signaturesMatch = NO; break;
}
}
}
这里循环也是从2开始的。举个例子来说明为什么从第二位开始比较。还是用之前的例子。
[UIView aspect_hookSelector:@selector(UIView:atIndex:) withOptions:AspectPositionAfter usingBlock:^(id<AspectInfo> aspects, UIView *view, NSInteger index)
{
NSLog(@"按钮点击了 %ld",index);
} error:nil];
这里我要替换的原方法是UIView:atIndex:,那么对应的Type是v@:@q。根据上面的分析,这里的blockSignature是之前调用转换出来的Type,应该是v@?@“”@“UIView"q。
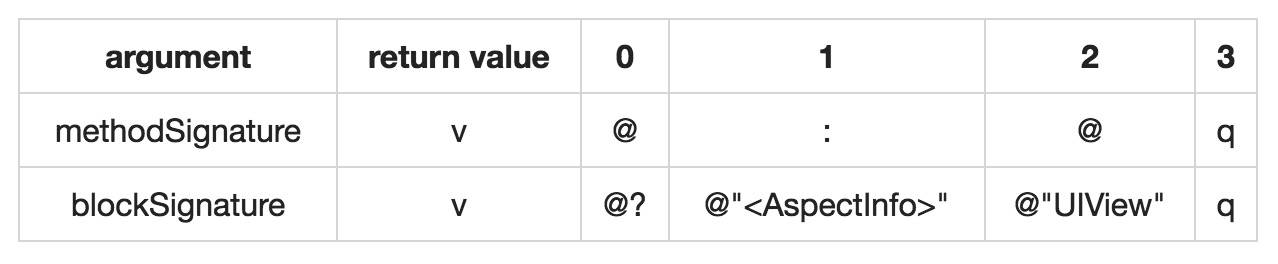
methodSignature 和 blockSignature 的return value都是void,所以对应的都是v。methodSignature的argument 0 是隐含参数 self,所以对应的是@。blockSignature的argument 0 是block,所以对应的是@?。methodSignature的argument 1 是隐含参数 _cmd,所以对应的是:。blockSignature的argument 1 是,所以对应的是@“”。从argument 2开始才是方法签名后面的对应可能出现差异,需要比较的参数列表。
最后
if (!signaturesMatch) {
NSString *description = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"Block signature %@ doesn't match %@.", blockSignature, methodSignature];
AspectError(AspectErrorIncompatibleBlockSignature, description);
return NO;
}
如果经过上面的比较signaturesMatch都为NO,那么就抛出error,Block无法匹配方法签名。
AspectIdentifier *identifier = nil;
if (blockSignature) {
identifier = [AspectIdentifier new];
identifier.selector = selector;
identifier.block = block;
identifier.blockSignature = blockSignature;
identifier.options = options;
identifier.object = object; // weak
}
return identifier;
如果这里匹配成功了,就会blockSignature全部都赋值给AspectIdentifier。这也就是为何AspectIdentifier里面有一个单独的属性NSMethodSignature的原因。
AspectIdentifier还有另外一个方法invokeWithInfo。
// Be extra paranoid. We already check that on hook registration.
if (numberOfArguments > originalInvocation.methodSignature.numberOfArguments) {
AspectLogError(@"Block has too many arguments. Not calling %@", info);
return NO;
}
注释也写清楚了,这个判断是强迫症患者写的,到了这里block里面的参数是不会大于原始方法的方法签名里面参数的个数的。
// The `self` of the block will be the AspectInfo. Optional.
if (numberOfArguments > 1) {
[blockInvocation setArgument:&info atIndex:1];
}
把AspectInfo存入到blockInvocation中。
void *argBuf = NULL;
for (NSUInteger idx = 2; idx < numberOfArguments; idx++) {
const char *type = [originalInvocation.methodSignature getArgumentTypeAtIndex:idx];
NSUInteger argSize;
NSGetSizeAndAlignment(type, &argSize, NULL);
if (!(argBuf = reallocf(argBuf, argSize))) {
AspectLogError(@"Failed to allocate memory for block invocation.");
return NO;
}
[originalInvocation getArgument:argBuf atIndex:idx];
[blockInvocation setArgument:argBuf atIndex:idx];
}
[blockInvocation invokeWithTarget:self.block];
这一段是循环把originalInvocation中取出参数,赋值到argBuf中,然后再赋值到blockInvocation里面。循环从2开始的原因上面已经说过了,这里不再赘述。最后把self.block赋值给blockInvocation的Target。
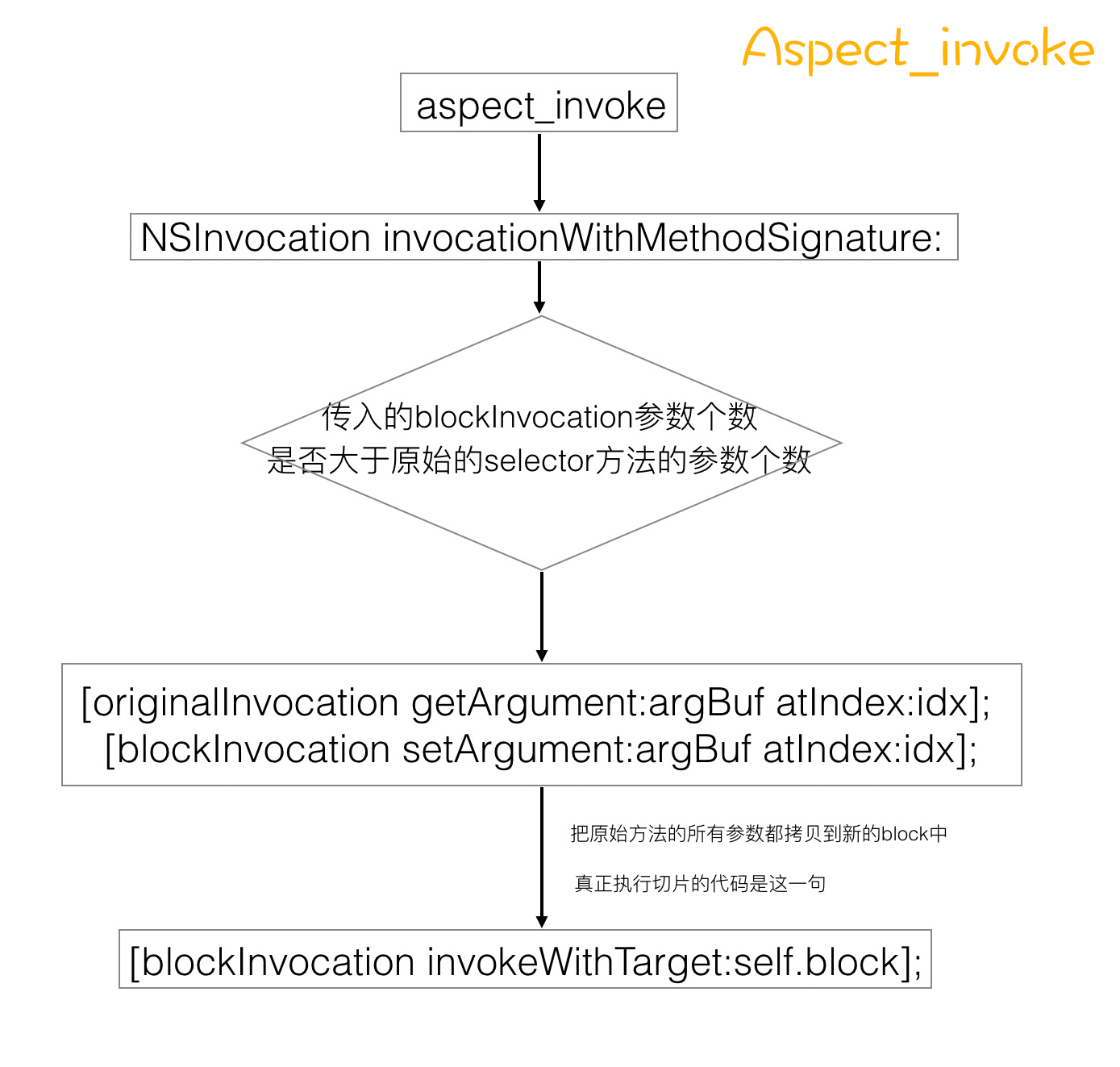
总结,AspectIdentifier是一个切片Aspect的具体内容。里面会包含了单个的 Aspect 的具体信息,包括执行时机,要执行 block 所需要用到的具体信息:包括方法签名、参数等等。初始化AspectIdentifier的过程实质是把我们传入的block打包成AspectIdentifier。
5. AspectsContainer
// Tracks all aspects for an object/class.
@interface AspectsContainer : NSObject
- (void)addAspect:(AspectIdentifier *)aspect withOptions:(AspectOptions)injectPosition;
- (BOOL)removeAspect:(id)aspect;
- (BOOL)hasAspects;
@property (atomic, copy) NSArray *beforeAspects;
@property (atomic, copy) NSArray *insteadAspects;
@property (atomic, copy) NSArray *afterAspects;
@end
对应实现
#pragma mark - AspectsContainer
@implementation AspectsContainer
- (BOOL)hasAspects {
return self.beforeAspects.count > 0 || self.insteadAspects.count > 0 || self.afterAspects.count > 0;
}
- (void)addAspect:(AspectIdentifier *)aspect withOptions:(AspectOptions)options {
NSParameterAssert(aspect);
NSUInteger position = options&AspectPositionFilter;
switch (position) {
case AspectPositionBefore: self.beforeAspects = [(self.beforeAspects ?:@[]) arrayByAddingObject:aspect]; break;
case AspectPositionInstead: self.insteadAspects = [(self.insteadAspects?:@[]) arrayByAddingObject:aspect]; break;
case AspectPositionAfter: self.afterAspects = [(self.afterAspects ?:@[]) arrayByAddingObject:aspect]; break;
}
}
- (BOOL)removeAspect:(id)aspect {
for (NSString *aspectArrayName in @[NSStringFromSelector(@selector(beforeAspects)),
NSStringFromSelector(@selector(insteadAspects)),
NSStringFromSelector(@selector(afterAspects))]) {
NSArray *array = [self valueForKey:aspectArrayName];
NSUInteger index = [array indexOfObjectIdenticalTo:aspect];
if (array && index != NSNotFound) {
NSMutableArray *newArray = [NSMutableArray arrayWithArray:array];
[newArray removeObjectAtIndex:index];
[self setValue:newArray forKey:aspectArrayName];
return YES;
}
}
return NO;
}
- (NSString *)description {
return [NSString stringWithFormat:@"<%@: %p, before:%@, instead:%@, after:%@>", self.class, self, self.beforeAspects, self.insteadAspects, self.afterAspects];
}
@end
AspectsContainer比较好理解。addAspect会按照切面的时机分别把切片Aspects放到对应的数组里面。removeAspects会循环移除所有的Aspects。hasAspects判断是否有Aspects。
AspectsContainer是一个对象或者类的所有的 Aspects 的容器。所有会有两种容器。
值得我们注意的是这里数组是通过Atomic修饰的。关于Atomic需要注意在默认情况下,由编译器所合成的方法会通过锁定机制确保其原子性(Atomicity)。如果属性具备nonatomic特质,则不需要同步锁。
6. AspectTracker

@interface AspectTracker : NSObject
- (id)initWithTrackedClass:(Class)trackedClass;
@property (nonatomic, strong) Class trackedClass;
@property (nonatomic, readonly) NSString *trackedClassName;
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSMutableSet *selectorNames;
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSMutableDictionary *selectorNamesToSubclassTrackers;
- (void)addSubclassTracker:(AspectTracker *)subclassTracker hookingSelectorName:(NSString *)selectorName;
- (void)removeSubclassTracker:(AspectTracker *)subclassTracker hookingSelectorName:(NSString *)selectorName;
- (BOOL)subclassHasHookedSelectorName:(NSString *)selectorName;
- (NSSet *)subclassTrackersHookingSelectorName:(NSString *)selectorName;
@end
对应实现
@implementation AspectTracker
- (id)initWithTrackedClass:(Class)trackedClass {
if (self = [super init]) {
_trackedClass = trackedClass;
_selectorNames = [NSMutableSet new];
_selectorNamesToSubclassTrackers = [NSMutableDictionary new];
}
return self;
}
- (BOOL)subclassHasHookedSelectorName:(NSString *)selectorName {
return self.selectorNamesToSubclassTrackers[selectorName] != nil;
}
- (void)addSubclassTracker:(AspectTracker *)subclassTracker hookingSelectorName:(NSString *)selectorName {
NSMutableSet *trackerSet = self.selectorNamesToSubclassTrackers[selectorName];
if (!trackerSet) {
trackerSet = [NSMutableSet new];
self.selectorNamesToSubclassTrackers[selectorName] = trackerSet;
}
[trackerSet addObject:subclassTracker];
}
- (void)removeSubclassTracker:(AspectTracker *)subclassTracker hookingSelectorName:(NSString *)selectorName {
NSMutableSet *trackerSet = self.selectorNamesToSubclassTrackers[selectorName];
[trackerSet removeObject:subclassTracker];
if (trackerSet.count == 0) {
[self.selectorNamesToSubclassTrackers removeObjectForKey:selectorName];
}
}
- (NSSet *)subclassTrackersHookingSelectorName:(NSString *)selectorName {
NSMutableSet *hookingSubclassTrackers = [NSMutableSet new];
for (AspectTracker *tracker in self.selectorNamesToSubclassTrackers[selectorName]) {
if ([tracker.selectorNames containsObject:selectorName]) {
[hookingSubclassTrackers addObject:tracker];
}
[hookingSubclassTrackers unionSet:[tracker subclassTrackersHookingSelectorName:selectorName]];
}
return hookingSubclassTrackers;
}
- (NSString *)trackedClassName {
return NSStringFromClass(self.trackedClass);
}
- (NSString *)description {
return [NSString stringWithFormat:@"<%@: %@, trackedClass: %@, selectorNames:%@, subclass selector names: %@>", self.class, self, NSStringFromClass(self.trackedClass), self.selectorNames, self.selectorNamesToSubclassTrackers.allKeys];
}
@end
AspectTracker这个类是用来跟踪要被hook的类。trackedClass是被追踪的类。trackedClassName是被追踪类的类名。selectorNames是一个NSMutableSet,这里会记录要被hook替换的方法名,用NSMutableSet是为了防止重复替换方法。selectorNamesToSubclassTrackers是一个字典,key是hookingSelectorName,value是装满AspectTracker的NSMutableSet。
addSubclassTracker方法是把AspectTracker加入到对应selectorName的集合中。removeSubclassTracker方法是把AspectTracker从对应的selectorName的集合中移除。subclassTrackersHookingSelectorName方法是一个并查集,传入一个selectorName,通过递归查找,找到所有包含这个selectorName的set,最后把这些set合并在一起作为返回值返回。
四. Aspects hook前的准备工作

Aspects 库中就两个函数,一个是针对类的,一个是针对实例的。
+ (id<AspectToken>)aspect_hookSelector:(SEL)selector
withOptions:(AspectOptions)options
usingBlock:(id)block
error:(NSError **)error {
return aspect_add((id)self, selector, options, block, error);
}
- (id<AspectToken>)aspect_hookSelector:(SEL)selector
withOptions:(AspectOptions)options
usingBlock:(id)block
error:(NSError **)error {
return aspect_add(self, selector, options, block, error);
}
两个方法的实现都是调用同一个方法aspect_add,只是传入的参数不同罢了。所以我们只要从aspect_add开始研究即可。
- aspect_hookSelector:(SEL)selector withOptions:(AspectOptions)options usingBlock:(id)block error:(NSError **)error
└── aspect_add(self, selector, options, block, error);
└── aspect_performLocked
├── aspect_isSelectorAllowedAndTrack
└── aspect_prepareClassAndHookSelector
这是函数调用栈。从aspect_add开始研究。
static id aspect_add(id self, SEL selector, AspectOptions options, id block, NSError **error) {
NSCParameterAssert(self);
NSCParameterAssert(selector);
NSCParameterAssert(block);
__block AspectIdentifier *identifier = nil;
aspect_performLocked(^{
if (aspect_isSelectorAllowedAndTrack(self, selector, options, error)) {
AspectsContainer *aspectContainer = aspect_getContainerForObject(self, selector);
identifier = [AspectIdentifier identifierWithSelector:selector object:self options:options block:block error:error];
if (identifier) {
[aspectContainer addAspect:identifier withOptions:options];
// Modify the class to allow message interception.
aspect_prepareClassAndHookSelector(self, selector, error);
}
}
});
return identifier;
}
aspect_add函数一共5个入参,第一个参数是self,selector是外面传进来需要hook的SEL,options是切片的时间,block是切片的执行方法,最后的error是错误。
aspect_performLocked是一个自旋锁。自旋锁是效率比较高的一种锁,相比@synchronized来说效率高得多。
static void aspect_performLocked(dispatch_block_t block) {
static OSSpinLock aspect_lock = OS_SPINLOCK_INIT;
OSSpinLockLock(&aspect_lock);
block();
OSSpinLockUnlock(&aspect_lock);
}
如果对iOS中8大锁不了解的,可以看以下两篇文章
iOS 常见知识点(三):Lock
深入理解 iOS 开发中的锁

但是自旋锁也是有可能出现问题的: 如果一个低优先级的线程获得锁并访问共享资源,这时一个高优先级的线程也尝试获得这个锁,它会处于 spin lock 的忙等(busy-wait)状态从而占用大量 CPU。此时低优先级线程无法与高优先级线程争夺 CPU 时间,从而导致任务迟迟完不成、无法释放 lock。不再安全的 OSSpinLock
OSSpinLock的问题在于,如果访问这个所的线程不是同一优先级的话,会有死锁的潜在风险。
这里暂时认为是相同优先级的线程,所以OSSpinLock保证了线程安全。也就是说aspect_performLocked是保护了block的线程安全。
现在就剩下aspect_isSelectorAllowedAndTrack函数和aspect_prepareClassAndHookSelector函数了。
接下来先看看aspect_isSelectorAllowedAndTrack函数实现过程。
static NSSet *disallowedSelectorList;
static dispatch_once_t pred;
dispatch_once(&pred, ^{
disallowedSelectorList = [NSSet setWithObjects:@"retain", @"release", @"autorelease", @"forwardInvocation:", nil];
});
先定义了一个NSSet,这里面是一个“黑名单”,是不允许hook的函数名。retain, release, autorelease, forwardInvocation:是不允许被hook的。
NSString *selectorName = NSStringFromSelector(selector);
if ([disallowedSelectorList containsObject:selectorName]) {
NSString *errorDescription = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"Selector %@ is blacklisted.", selectorName];
AspectError(AspectErrorSelectorBlacklisted, errorDescription);
return NO;
}
当检测到selector的函数名是黑名单里面的函数名,立即报错。
AspectOptions position = options&AspectPositionFilter;
if ([selectorName isEqualToString:@"dealloc"] && position != AspectPositionBefore) {
NSString *errorDesc = @"AspectPositionBefore is the only valid position when hooking dealloc.";
AspectError(AspectErrorSelectorDeallocPosition, errorDesc);
return NO;
}
再次检查如果要切片dealloc,切片时间只能在dealloc之前,如果不是AspectPositionBefore,也要报错。
if (![self respondsToSelector:selector] && ![self.class instancesRespondToSelector:selector]) {
NSString *errorDesc = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"Unable to find selector -[%@ %@].", NSStringFromClass(self.class), selectorName];
AspectError(AspectErrorDoesNotRespondToSelector, errorDesc);
return NO;
}
当selector不在黑名单里面了,如果切片是dealloc,且selector在其之前了。这时候就该判断该方法是否存在。如果self和self.class里面都找不到该selector,会报错找不到该方法。
if (class_isMetaClass(object_getClass(self))) {
Class klass = [self class];
NSMutableDictionary *swizzledClassesDict = aspect_getSwizzledClassesDict();
Class currentClass = [self class];
AspectTracker *tracker = swizzledClassesDict[currentClass];
if ([tracker subclassHasHookedSelectorName:selectorName]) {
NSSet *subclassTracker = [tracker subclassTrackersHookingSelectorName:selectorName];
NSSet *subclassNames = [subclassTracker valueForKey:@"trackedClassName"];
NSString *errorDescription = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"Error: %@ already hooked subclasses: %@. A method can only be hooked once per class hierarchy.", selectorName, subclassNames];
AspectError(AspectErrorSelectorAlreadyHookedInClassHierarchy, errorDescription);
return NO;
}
class_isMetaClass 先判断是不是元类。接下来的判断都是判断元类里面能否允许被替换方法。
subclassHasHookedSelectorName会判断当前tracker的subclass里面是否包含selectorName。因为一个方法在一个类的层级里面只能被hook一次。如果已经tracker里面已经包含了一次,那么会报错。
do {
tracker = swizzledClassesDict[currentClass];
if ([tracker.selectorNames containsObject:selectorName]) {
if (klass == currentClass) {
// Already modified and topmost!
return YES;
}
NSString *errorDescription = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"Error: %@ already hooked in %@. A method can only be hooked once per class hierarchy.", selectorName, NSStringFromClass(currentClass)];
AspectError(AspectErrorSelectorAlreadyHookedInClassHierarchy, errorDescription);
return NO;
}
} while ((currentClass = class_getSuperclass(currentClass)));
在这个do-while循环中,currentClass = class_getSuperclass(currentClass)这个判断会从currentClass的superclass开始,一直往上找,直到这个类为根类NSObject。
currentClass = klass;
AspectTracker *subclassTracker = nil;
do {
tracker = swizzledClassesDict[currentClass];
if (!tracker) {
tracker = [[AspectTracker alloc] initWithTrackedClass:currentClass];
swizzledClassesDict[(id<NSCopying>)currentClass] = tracker;
}
if (subclassTracker) {
[tracker addSubclassTracker:subclassTracker hookingSelectorName:selectorName];
} else {
[tracker.selectorNames addObject:selectorName];
}
// All superclasses get marked as having a subclass that is modified.
subclassTracker = tracker;
}while ((currentClass = class_getSuperclass(currentClass)));
经过上面合法性hook判断和类方法不允许重复替换的检查后,到此,就可以把要hook的信息记录下来,用AspectTracker标记。在标记过程中,一旦子类被更改,父类也需要跟着一起被标记。do-while的终止条件还是currentClass = class_getSuperclass(currentClass)。
以上是元类的类方法hook判断合法性的代码。
如果不是元类,只要不是hook这"retain”, “release”, “autorelease”, “forwardInvocation:“4种方法,而且hook “dealloc”方法的时机必须是before,并且selector能被找到,那么方法就可以被hook。
通过了selector是否能被hook合法性的检查之后,就要获取或者创建AspectsContainer容器了。
// Loads or creates the aspect container.
static AspectsContainer *aspect_getContainerForObject(NSObject *self, SEL selector) {
NSCParameterAssert(self);
SEL aliasSelector = aspect_aliasForSelector(selector);
AspectsContainer *aspectContainer = objc_getAssociatedObject(self, aliasSelector);
if (!aspectContainer) {
aspectContainer = [AspectsContainer new];
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, aliasSelector, aspectContainer, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN);
}
return aspectContainer;
}
在读取或者创建AspectsContainer之前,第一步是先标记一下selector。
static SEL aspect_aliasForSelector(SEL selector) {
NSCParameterAssert(selector);
return NSSelectorFromString([AspectsMessagePrefix stringByAppendingFormat:@"_%@", NSStringFromSelector(selector)]);
}
在全局代码里面定义了一个常量字符串
static NSString *const AspectsMessagePrefix = @"aspects_";
用这个字符串标记所有的selector,都加上前缀"aspects_"。然后获得其对应的AssociatedObject关联对象,如果获取不到,就创建一个关联对象。最终得到selector有"aspects_“前缀,对应的aspectContainer。
得到了aspectContainer之后,就可以开始准备我们要hook方法的一些信息。这些信息都装在AspectIdentifier中,所以我们需要新建一个AspectIdentifier。
调用AspectIdentifier的instancetype方法,创建一个新的AspectIdentifier
+ (instancetype)identifierWithSelector:(SEL)selector object:(id)object options:(AspectOptions)options block:(id)block error:(NSError **)error
这个instancetype方法,只有一种情况会创建失败,那就是aspect_isCompatibleBlockSignature方法返回NO。返回NO就意味着,我们要替换的方法block和要替换的原方法,两者的方法签名是不相符的。(这个函数在上面详解过了,这里不再赘述)。方法签名匹配成功之后,就会创建好一个AspectIdentifier。
[aspectContainer addAspect:identifier withOptions:options];
aspectContainer容器会把它加入到容器中。完成了容器和AspectIdentifier初始化之后,就可以开始准备进行hook了。通过options选项分别添加到容器中的beforeAspects,insteadAspects,afterAspects这三个数组
// Modify the class to allow message interception.
aspect_prepareClassAndHookSelector(self, selector, error);
小结一下,aspect_add干了一些什么准备工作:
- 首先调用aspect_performLocked ,利用自旋锁,保证整个操作的线程安全
- 接着调用aspect_isSelectorAllowedAndTrack对传进来的参数进行强校验,保证参数合法性。
- 接着创建AspectsContainer容器,利用AssociatedObject关联对象动态添加到NSObject分类中作为属性的。
- 再由入参selector,option,创建AspectIdentifier实例。AspectIdentifier主要包含了单个的 Aspect的具体信息,包括执行时机,要执行block 所需要用到的具体信息。
- 再将单个的 AspectIdentifier 的具体信息加到属性AspectsContainer容器中。通过options选项分别添加到容器中的beforeAspects,insteadAspects,afterAspects这三个数组。
- 最后调用prepareClassAndHookSelector准备hook。
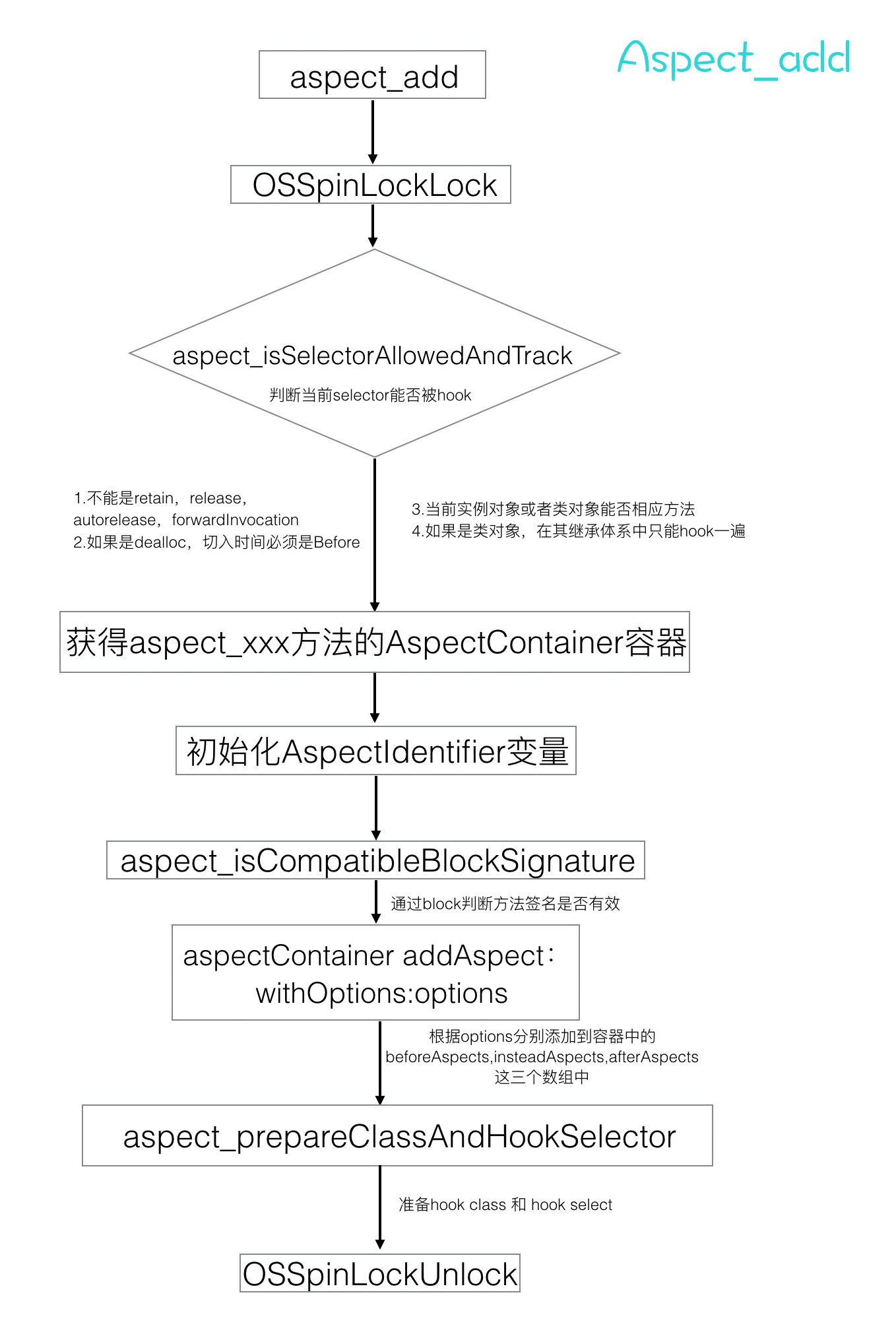
五. Aspects hook过程详解
先看看函数调用栈的情况
- aspect_prepareClassAndHookSelector(self, selector, error);
├── aspect_hookClass(self, error)
│ ├──aspect_swizzleClassInPlace
│ ├──aspect_swizzleForwardInvocation
│ │ └──__ASPECTS_ARE_BEING_CALLED__
│ │ ├──aspect_aliasForSelector
│ │ ├──aspect_getContainerForClass
│ │ ├──aspect_invoke
│ │ └──aspect_remove
│ └── aspect_hookedGetClass
├── aspect_isMsgForwardIMP
├──aspect_aliasForSelector(selector)
└── aspect_getMsgForwardIMP
从调用栈可以看出,Aspects hook过程主要分4个阶段,hookClass,ASPECTS_ARE_BEING_CALLED,prepareClassAndHookSelector,remove。

1. hookClass
NSCParameterAssert(self);
Class statedClass = self.class;
Class baseClass = object_getClass(self);
NSString *className = NSStringFromClass(baseClass);
statedClass 和 baseClass是有区别的的。
Class object_getClass(id obj)
{
if (obj) return obj->getIsa();
else return Nil;
}
+ (Class)class {
return self;
}
statedClass 是获取类对象,baseClass是获取到类的isa。
// Already subclassed
if ([className hasSuffix:AspectsSubclassSuffix]) {
return baseClass;
// We swizzle a class object, not a single object.
}else if (class_isMetaClass(baseClass)) {
return aspect_swizzleClassInPlace((Class)self);
// Probably a KVO'ed class. Swizzle in place. Also swizzle meta classes in place.
}else if (statedClass != baseClass) {
return aspect_swizzleClassInPlace(baseClass);
}
先判断是用来className是否包含hasSuffix:AspectsSubclassSuffix
static NSString *const AspectsSubclassSuffix = @"_Aspects_";
如果包含了@"_Aspects_“后缀,代表该类已经被hook过了,直接return。 如果不包含@"_Aspects_“后缀,再判断是否是baseClass是否是元类,如果是元类,调用aspect_swizzleClassInPlace。如果也不是元类,再判断statedClass 和 baseClass是否相等,如果不相等,说明为KVO过的对象,因为KVO的对象isa指针会指向一个中间类。对KVO中间类调用aspect_swizzleClassInPlace。
static Class aspect_swizzleClassInPlace(Class klass) {
NSCParameterAssert(klass);
NSString *className = NSStringFromClass(klass);
_aspect_modifySwizzledClasses(^(NSMutableSet *swizzledClasses) {
if (![swizzledClasses containsObject:className]) {
aspect_swizzleForwardInvocation(klass);
[swizzledClasses addObject:className];
}
});
return klass;
}
_aspect_modifySwizzledClasses会传入一个入参为(NSMutableSet *swizzledClasses)的block,block里面就是判断在这个Set里面是否包含当前的ClassName,如果不包含,就调用aspect_swizzleForwardInvocation()方法,并把className加入到Set集合里面。
static void _aspect_modifySwizzledClasses(void (^block)(NSMutableSet *swizzledClasses)) {
static NSMutableSet *swizzledClasses;
static dispatch_once_t pred;
dispatch_once(&pred, ^{
swizzledClasses = [NSMutableSet new];
});
@synchronized(swizzledClasses) {
block(swizzledClasses);
}
}
_aspect_modifySwizzledClasses方法里面保证了swizzledClasses这个Set集合是全局唯一的,并且给传入的block加上了线程锁@synchronized( ),保证了block调用中线程是安全的。
关于调用aspect_swizzleForwardInvocation,将原IMP指向forwardInvocation是下个阶段的事情,我们先把hookClass看完。
// Default case. Create dynamic subclass.
const char *subclassName = [className stringByAppendingString:AspectsSubclassSuffix].UTF8String;
Class subclass = objc_getClass(subclassName);
if (subclass == nil) {
subclass = objc_allocateClassPair(baseClass, subclassName, 0);
if (subclass == nil) {
NSString *errrorDesc = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"objc_allocateClassPair failed to allocate class %s.", subclassName];
AspectError(AspectErrorFailedToAllocateClassPair, errrorDesc);
return nil;
}
aspect_swizzleForwardInvocation(subclass);
aspect_hookedGetClass(subclass, statedClass);
aspect_hookedGetClass(object_getClass(subclass), statedClass);
objc_registerClassPair(subclass);
}
object_setClass(self, subclass);
当className没有包含@"_Aspects_“后缀,并且也不是元类,也不是KVO的中间类,即statedClass = = baseClass 的情况,于是,默认的新建一个子类subclass。
到此,我们可以了解到Aspects的设计思想,hook 是在runtime中动态创建子类的基础上实现的。所有的 swizzling 操作都发生在子类,这样做的好处是你不需要去更改对象本身的类,也就是,当你在 remove aspects 的时候,如果发现当前对象的 aspect 都被移除了,那么,你可以将 isa 指针重新指回对象本身的类,从而消除了该对象的 swizzling ,同时也不会影响到其他该类的不同对象)这样对原来替换的类或者对象没有任何影响而且可以在子类基础上新增或者删除aspect。
新建的类的名字,会先加上AspectsSubclassSuffix后缀,即在className后面加上@"_Aspects_",标记成子类。再调用objc_getClass方法,创建这个子类。
/***********************************************************************
* objc_getClass. Return the id of the named class. If the class does
* not exist, call _objc_classLoader and then objc_classHandler, either of
* which may create a new class.
* Warning: doesn't work if aClassName is the name of a posed-for class's isa!
**********************************************************************/
Class objc_getClass(const char *aClassName)
{
if (!aClassName) return Nil;
// NO unconnected, YES class handler
return look_up_class(aClassName, NO, YES);
}
objc_getClass会调用look_up_class方法。
/***********************************************************************
* look_up_class
* Look up a class by name, and realize it.
* Locking: acquires runtimeLock
**********************************************************************/
Class look_up_class(const char *name,
bool includeUnconnected __attribute__((unused)),
bool includeClassHandler __attribute__((unused)))
{
if (!name) return nil;
Class result;
bool unrealized;
{
rwlock_reader_t lock(runtimeLock);
result = getClass(name);
unrealized = result && !result->isRealized();
}
if (unrealized) {
rwlock_writer_t lock(runtimeLock);
realizeClass(result);
}
return result;
}
这个方法会去查看有没有实现叫name的class,查看过程中会用到rwlock_reader_t lock(runtimeLock),读写锁,底层是用pthread_rwlock_t实现的。
由于是我们刚刚新建的一个子类名,很有可能是objc_getClass()返回nil。那么我们需要新建这个子类。调用objc_allocateClassPair()方法。
/***********************************************************************
* objc_allocateClassPair
* fixme
* Locking: acquires runtimeLock
**********************************************************************/
Class objc_allocateClassPair(Class superclass, const char *name,
size_t extraBytes)
{
Class cls, meta;
rwlock_writer_t lock(runtimeLock);
// Fail if the class name is in use.
// Fail if the superclass isn't kosher.
if (getClass(name) || !verifySuperclass(superclass, true/*rootOK*/)) {
return nil;
}
// Allocate new classes.
cls = alloc_class_for_subclass(superclass, extraBytes);
meta = alloc_class_for_subclass(superclass, extraBytes);
// fixme mangle the name if it looks swift-y?
objc_initializeClassPair_internal(superclass, name, cls, meta);
return cls;
}
调用objc_allocateClassPair会新建一个子类,它的父类是入参superclass。
如果新建的子类subclass = = nil,就会报错,objc_allocateClassPair failed to allocate class。
aspect_swizzleForwardInvocation(subclass)这是下一阶段的事情,主要作用是替换当前类forwardInvocation方法的实现为__ASPECTS_ARE_BEING_CALLED__,先略过。
接着调用aspect_hookedGetClass( ) 方法。
static void aspect_hookedGetClass(Class class, Class statedClass) {
NSCParameterAssert(class);
NSCParameterAssert(statedClass);
Method method = class_getInstanceMethod(class, @selector(class));
IMP newIMP = imp_implementationWithBlock(^(id self) {
return statedClass;
});
class_replaceMethod(class, @selector(class), newIMP, method_getTypeEncoding(method));
}
aspect_hookedGetClass方法是把class的实例方法替换成返回statedClass,也就是说把调用class时候的isa指向了statedClass了。
aspect_hookedGetClass(subclass, statedClass);
aspect_hookedGetClass(object_getClass(subclass), statedClass);
这两句的意图我们也就明白了。
第一句是把subclass的isa指向了statedClass,第二句是把subclass的元类的isa,也指向了statedClass。
最后调用objc_registerClassPair( ) 注册刚刚新建的子类subclass,再调用object_setClass(self, subclass);把当前self的isa指向子类subclass。
至此,hookClass阶段就完成了,成功的把self hook成了其子类 xxx_Aspects_。
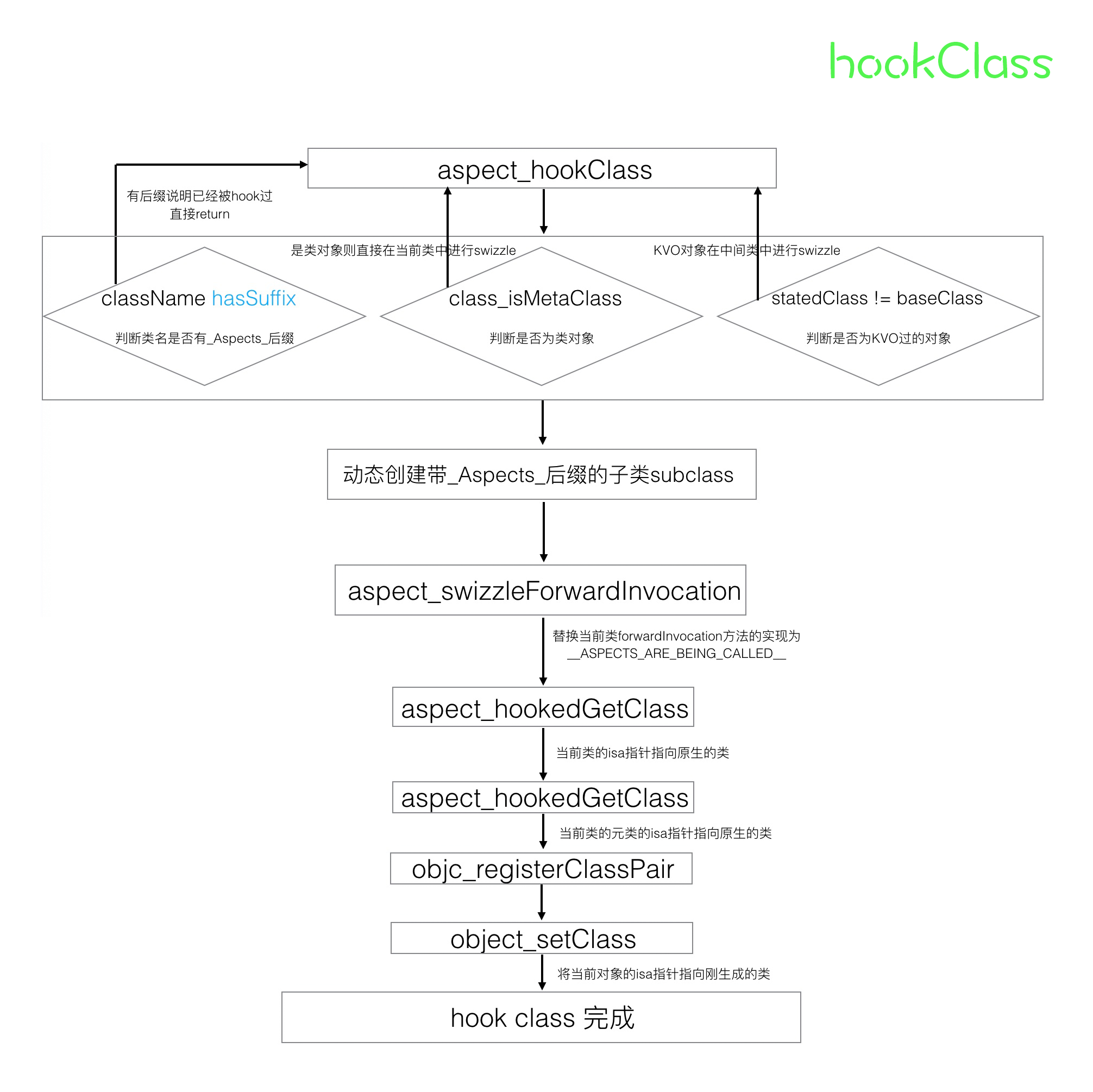
2. ASPECTS_ARE_BEING_CALLED
在上一阶段hookClass的时候,有几处都调用了aspect_swizzleForwardInvocation方法。
static NSString *const AspectsForwardInvocationSelectorName = @"__aspects_forwardInvocation:";
static void aspect_swizzleForwardInvocation(Class klass) {
NSCParameterAssert(klass);
// If there is no method, replace will act like class_addMethod.
IMP originalImplementation = class_replaceMethod(klass, @selector(forwardInvocation:), (IMP)__ASPECTS_ARE_BEING_CALLED__, "v@:@");
if (originalImplementation) {
class_addMethod(klass, NSSelectorFromString(AspectsForwardInvocationSelectorName), originalImplementation, "v@:@");
}
AspectLog(@"Aspects: %@ is now aspect aware.", NSStringFromClass(klass));
}
aspect_swizzleForwardInvocation就是整个Aspects hook方法的开始。
/***********************************************************************
* class_replaceMethod
**********************************************************************/
IMP class_replaceMethod(Class cls, SEL name, IMP imp, const char *types)
{
if (!cls) return nil;
return _class_addMethod(cls, name, imp, types, YES);
}
调用class_replaceMethod方法,实际底层实现是调用_class_addMethod方法。
static IMP _class_addMethod(Class cls, SEL name, IMP imp,
const char *types, bool replace)
{
old_method *m;
IMP result = nil;
if (!types) types = "";
mutex_locker_t lock(methodListLock);
if ((m = _findMethodInClass(cls, name))) {
// already exists
// fixme atomic
result = method_getImplementation((Method)m);
if (replace) {
method_setImplementation((Method)m, imp);
}
} else {
// fixme could be faster
old_method_list *mlist =
(old_method_list *)calloc(sizeof(old_method_list), 1);
mlist->obsolete = fixed_up_method_list;
mlist->method_count = 1;
mlist->method_list[0].method_name = name;
mlist->method_list[0].method_types = strdup(types);
if (!ignoreSelector(name)) {
mlist->method_list[0].method_imp = imp;
} else {
mlist->method_list[0].method_imp = (IMP)&_objc_ignored_method;
}
_objc_insertMethods(cls, mlist, nil);
if (!(cls->info & CLS_CONSTRUCTING)) {
flush_caches(cls, NO);
} else {
// in-construction class has no subclasses
flush_cache(cls);
}
result = nil;
}
return result;
}
从上述源码中,我们可以看到,先_findMethodInClass(cls, name),从cls中查找有没有name的方法。如果有,并且能找到对应的IMP的话,就进行替换method_setImplementation((Method)m, imp),把name方法的IMP替换成imp。这种方式_class_addMethod返回的是name方法对应的IMP,实际上就是我们替换完的imp。
如果在cls中没有找到name方法,那么就添加该方法,在mlist -> method_list[0] 的位置插入新的name方法,对应的IMP就是传入的imp。这种方式_class_addMethod返回的是nil。
回到aspect_swizzleForwardInvocation中,
IMP originalImplementation = class_replaceMethod(klass, @selector(forwardInvocation:), (IMP)__ASPECTS_ARE_BEING_CALLED__, "v@:@");
if (originalImplementation) {
class_addMethod(klass, NSSelectorFromString(AspectsForwardInvocationSelectorName), originalImplementation, "v@:@");
}
把forwardInvocation:的IMP替换成__ASPECTS_ARE_BEING_CALLED__ 。如果在klass里面找不到forwardInvocation:方法,就会新添加该方法。
由于子类本身并没有实现 forwardInvocation ,隐藏返回的 originalImplementation 将为空值,所以也不会生成 NSSelectorFromString(AspectsForwardInvocationSelectorName) 。所以还需要_class_addMethod会为我们添加了forwardInvocation:方法的实现
谢谢简书的大神 @zhao0 指点,这个坑在Aspects 1.4.1中已经修复了。
在aspect_swizzleForwardInvocation中,class_replaceMethod返回的是原方法的IMP,originalImplementation不为空的话说明原方法有实现,添加一个新方法__aspects_forwardInvocation:指向了原来的originalImplementation,在__ASPECTS_ARE_BEING_CALLED__那里如果不能处理,判断是否有实现__aspects_forwardInvocation,有的话就转发,这样就可以解决不兼容的问题。
如果originalImplementation返回的不是nil,就说明已经替换成功。替换完方法之后,我们在klass中再加入一个叫“__aspects_forwardInvocation:”的方法,对应的实现也是(IMP)__ASPECTS_ARE_BEING_CALLED__。
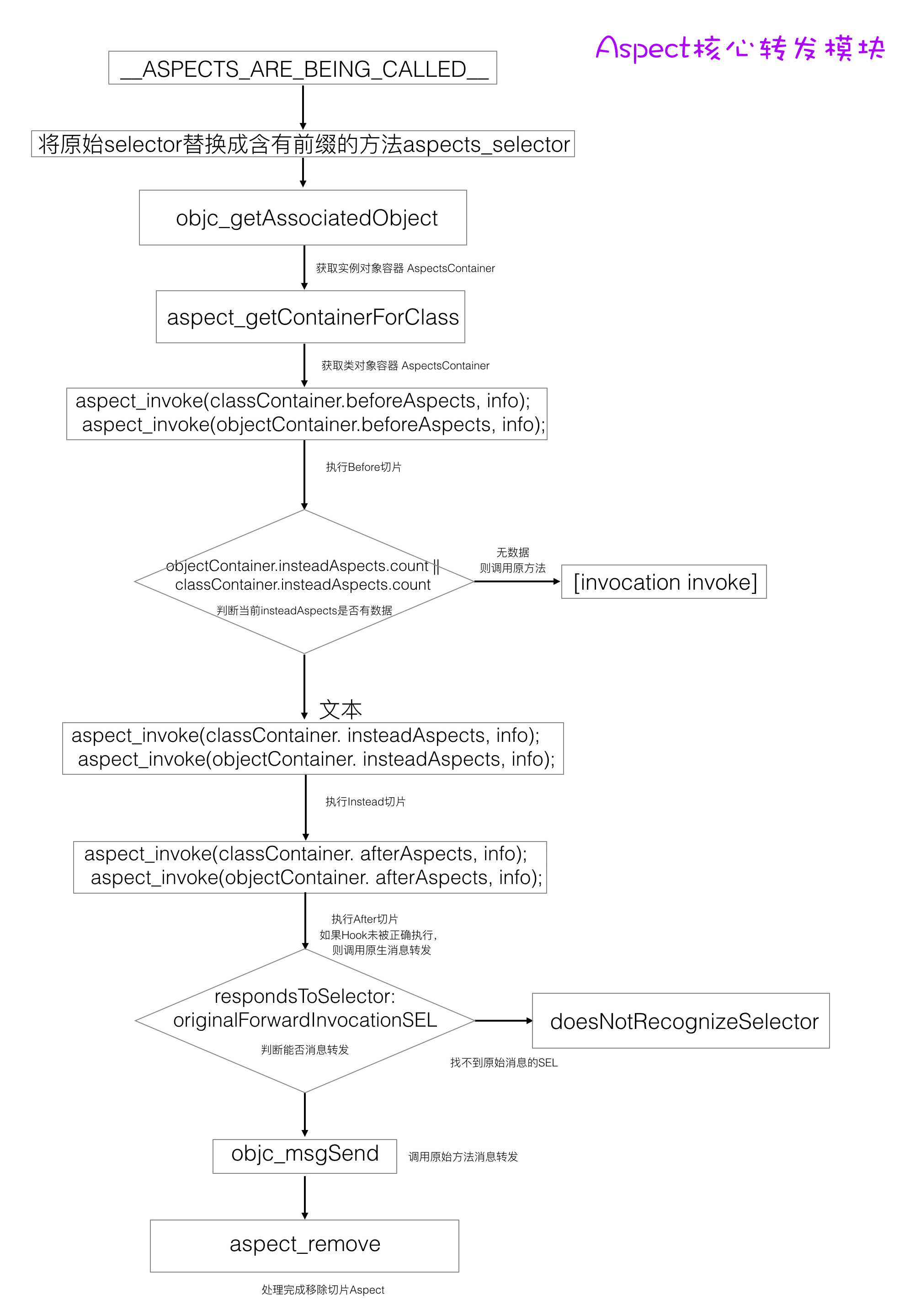
接下来就是整个Aspects的核心实现了:__ASPECTS_ARE_BEING_CALLED__
static void __ASPECTS_ARE_BEING_CALLED__(__unsafe_unretained NSObject *self, SEL selector, NSInvocation *invocation) {
NSCParameterAssert(self);
NSCParameterAssert(invocation);
SEL originalSelector = invocation.selector;
SEL aliasSelector = aspect_aliasForSelector(invocation.selector);
invocation.selector = aliasSelector;
AspectsContainer *objectContainer = objc_getAssociatedObject(self, aliasSelector);
AspectsContainer *classContainer = aspect_getContainerForClass(object_getClass(self), aliasSelector);
AspectInfo *info = [[AspectInfo alloc] initWithInstance:self invocation:invocation];
NSLog(@"%@",info.arguments);
NSArray *aspectsToRemove = nil;
…… ……
}
这一段是hook前的准备工作:
- 获取原始的selector
- 获取带有aspects_xxxx前缀的方法
- 替换selector
- 获取实例对象的容器objectContainer,这里是之前aspect_add关联过的对象。
- 获取获得类对象容器classContainer
- 初始化AspectInfo,传入self、invocation参数
// Before hooks.
aspect_invoke(classContainer.beforeAspects, info);
aspect_invoke(objectContainer.beforeAspects, info);
调用宏定义执行Aspects切片功能
#define aspect_invoke(aspects, info) \
for (AspectIdentifier *aspect in aspects) {\
[aspect invokeWithInfo:info];\
if (aspect.options & AspectOptionAutomaticRemoval) { \
aspectsToRemove = [aspectsToRemove?:@[] arrayByAddingObject:aspect]; \
} \
}
之所以这里用一个宏定义来实现里面的功能,是为了获得一个更加清晰的堆栈信息。
宏定义里面就做了两件事情,一个是执行了[aspect invokeWithInfo:info]方法,一个是把需要remove的Aspects加入等待被移除的数组中。
[aspect invokeWithInfo:info]方法在上篇里面详细分析过了其实现,这个函数的主要目的是把blockSignature初始化blockSignature得到invocation。然后处理参数,如果参数block中的参数大于1个,则把传入的AspectInfo放入blockInvocation中。然后从originalInvocation中取出参数给blockInvocation赋值。最后调用[blockInvocation invokeWithTarget:self.block];这里Target设置为self.block。也就执行了我们hook方法的block。
所以只要调用aspect_invoke(classContainer.Aspects, info);这个核心替换的方法,就能hook我们原有的SEL。对应的,函数第一个参数分别传入的是classContainer.beforeAspects、classContainer.insteadAspects、classContainer.afterAspects就能对应的实现before、instead、after对应时间的Aspects切片的hook。
// Instead hooks.
BOOL respondsToAlias = YES;
if (objectContainer.insteadAspects.count || classContainer.insteadAspects.count) {
aspect_invoke(classContainer.insteadAspects, info);
aspect_invoke(objectContainer.insteadAspects, info);
}else {
Class klass = object_getClass(invocation.target);
do {
if ((respondsToAlias = [klass instancesRespondToSelector:aliasSelector])) {
[invocation invoke];
break;
}
}while (!respondsToAlias && (klass = class_getSuperclass(klass)));
}
这一段代码是实现Instead hooks的。先判断当前insteadAspects是否有数据,如果没有数据则判断当前继承链是否能响应aspects_xxx方法,如果能,则直接调用aliasSelector。注意:这里的aliasSelector是原方法method
// After hooks.
aspect_invoke(classContainer.afterAspects, info);
aspect_invoke(objectContainer.afterAspects, info);
这两行是对应的执行After hooks的。原理如上。
至此,before、instead、after对应时间的Aspects切片的hook如果能被执行的,都执行完毕了。
如果hook没有被正常执行,那么就应该执行原来的方法。
// If no hooks are installed, call original implementation (usually to throw an exception)
if (!respondsToAlias) {
invocation.selector = originalSelector;
SEL originalForwardInvocationSEL = NSSelectorFromString(AspectsForwardInvocationSelectorName);
if ([self respondsToSelector:originalForwardInvocationSEL]) {
((void( *)(id, SEL, NSInvocation *))objc_msgSend)(self, originalForwardInvocationSEL, invocation);
}else {
[self doesNotRecognizeSelector:invocation.selector];
}
}
invocation.selector先换回原来的originalSelector,如果没有被hook成功,那么AspectsForwardInvocationSelectorName还能再拿到原来的IMP对应的SEL。如果能相应,就调用原来的SEL,否则就报出doesNotRecognizeSelector的错误。
[aspectsToRemove makeObjectsPerformSelector:@selector(remove)];
最后调用移除方法,移除hook。
3. prepareClassAndHookSelector
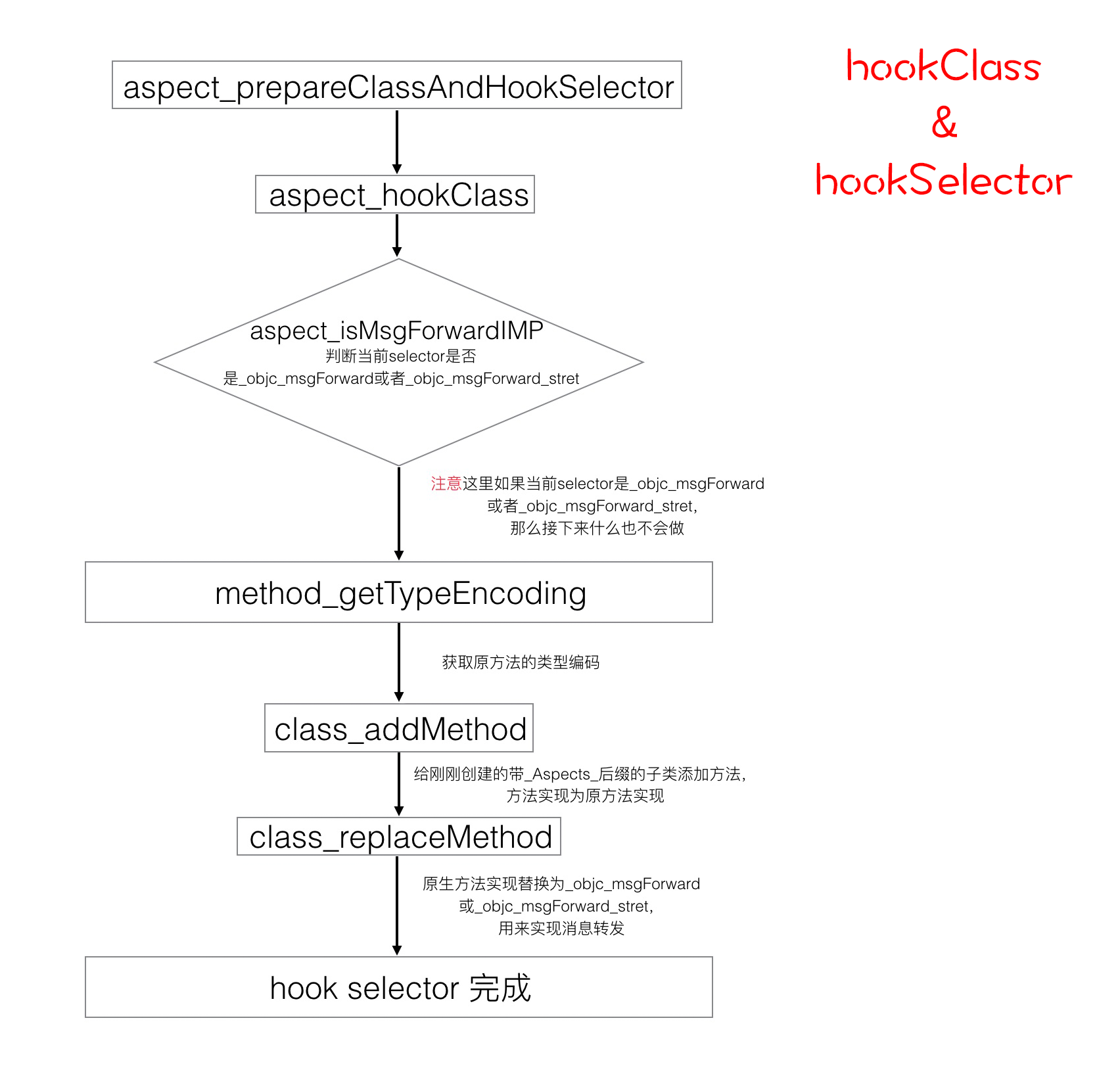
现在又要回到上篇中提到的aspect_prepareClassAndHookSelector方法中来了。
static void aspect_prepareClassAndHookSelector(NSObject *self, SEL selector, NSError **error) {
NSCParameterAssert(selector);
Class klass = aspect_hookClass(self, error);
Method targetMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(klass, selector);
IMP targetMethodIMP = method_getImplementation(targetMethod);
if (!aspect_isMsgForwardIMP(targetMethodIMP)) {
// Make a method alias for the existing method implementation, it not already copied.
const char *typeEncoding = method_getTypeEncoding(targetMethod);
SEL aliasSelector = aspect_aliasForSelector(selector);
if (![klass instancesRespondToSelector:aliasSelector]) {
__unused BOOL addedAlias = class_addMethod(klass, aliasSelector, method_getImplementation(targetMethod), typeEncoding);
NSCAssert(addedAlias, @"Original implementation for %@ is already copied to %@ on %@", NSStringFromSelector(selector), NSStringFromSelector(aliasSelector), klass);
}
// We use forwardInvocation to hook in.
class_replaceMethod(klass, selector, aspect_getMsgForwardIMP(self, selector), typeEncoding);
AspectLog(@"Aspects: Installed hook for -[%@ %@].", klass, NSStringFromSelector(selector));
}
}
klass是我们hook完原始的class之后得到的子类,名字是带有_Aspects_后缀的子类。因为它是当前类的子类,所以也可以从它这里获取到原有的selector的IMP。
static BOOL aspect_isMsgForwardIMP(IMP impl) {
return impl == _objc_msgForward
#if !defined(__arm64__)
|| impl == (IMP)_objc_msgForward_stret
#endif
;
}
这里是判断当前IMP是不是_objc_msgForward或者_objc_msgForward_stret,即判断当前IMP是不是消息转发。
如果不是消息转发,就先获取当前原始的selector对应的IMP的方法编码typeEncoding。
如果子类里面不能响应aspects_xxxx,就为klass添加aspects_xxxx方法,方法的实现为原生方法的实现。
Aspects整个hook的入口就是这句话:
class_replaceMethod(klass, selector, aspect_getMsgForwardIMP(self, selector), typeEncoding);
由于我们将slector指向_objc_msgForward 和_objc_msgForward_stret,可想而知,当selector被执行的时候,也会触发消息转发从而进入forwardInvocation,而我们又对forwardInvacation进行了swizzling,因此,最终转入我们自己的处理逻辑代码中。
4. aspect_remove
aspect_remove整个销毁过程的函数调用栈
- aspect_remove(AspectIdentifier *aspect, NSError **error)
└── aspect_cleanupHookedClassAndSelector
├──aspect_deregisterTrackedSelector
│ └── aspect_getSwizzledClassesDict
├──aspect_destroyContainerForObject
└── aspect_undoSwizzleClassInPlace
└── _aspect_modifySwizzledClasses
└──aspect_undoSwizzleForwardInvocation
static BOOL aspect_remove(AspectIdentifier *aspect, NSError **error) {
NSCAssert([aspect isKindOfClass:AspectIdentifier.class], @"Must have correct type.");
__block BOOL success = NO;
aspect_performLocked(^{
id self = aspect.object; // strongify
if (self) {
AspectsContainer *aspectContainer = aspect_getContainerForObject(self, aspect.selector);
success = [aspectContainer removeAspect:aspect];
aspect_cleanupHookedClassAndSelector(self, aspect.selector);
// destroy token
aspect.object = nil;
aspect.block = nil;
aspect.selector = NULL;
}else {
NSString *errrorDesc = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"Unable to deregister hook. Object already deallocated: %@", aspect];
AspectError(AspectErrorRemoveObjectAlreadyDeallocated, errrorDesc);
}
});
return success;
}
aspect_remove 是整个 aspect_add的逆过程。 aspect_performLocked是保证线程安全。把AspectsContainer都置为空,remove最关键的过程就是aspect_cleanupHookedClassAndSelector(self, aspect.selector);移除之前hook的class和selector。
static void aspect_cleanupHookedClassAndSelector(NSObject *self, SEL selector) {
NSCParameterAssert(self);
NSCParameterAssert(selector);
Class klass = object_getClass(self);
BOOL isMetaClass = class_isMetaClass(klass);
if (isMetaClass) {
klass = (Class)self;
}
…… ……
}
klass是现在的class,如果是元类,就转换成元类。
// Check if the method is marked as forwarded and undo that.
Method targetMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(klass, selector);
IMP targetMethodIMP = method_getImplementation(targetMethod);
if (aspect_isMsgForwardIMP(targetMethodIMP)) {
// Restore the original method implementation.
const char *typeEncoding = method_getTypeEncoding(targetMethod);
SEL aliasSelector = aspect_aliasForSelector(selector);
Method originalMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(klass, aliasSelector);
IMP originalIMP = method_getImplementation(originalMethod);
NSCAssert(originalMethod, @"Original implementation for %@ not found %@ on %@", NSStringFromSelector(selector), NSStringFromSelector(aliasSelector), klass);
class_replaceMethod(klass, selector, originalIMP, typeEncoding);
AspectLog(@"Aspects: Removed hook for -[%@ %@].", klass, NSStringFromSelector(selector));
}
先回复MsgForward消息转发函数,获得方法签名,然后把原始转发方法替换回我们hook过的方法。
这里有一个需要注意的问题。
如果当前Student有2个实例,stu1和stu2,并且他们都同时hook了相同的方法study( ),stu2在执行完aspect_remove,把stu2的study( )方法还原了。这里会把stu1的study( )方法也还原了。因为remove方法这个操作是对整个类的所有实例都生效的。
要想每个实例还原各自的方法,不影响其他实例,上述这段代码删除即可。因为在执行 remove 操作的时候,其实和这个对象相关的数据结构都已经被清除了,即使不去恢复 stu2 的study( ) 的执行,在进入 __ASPECTS_ARE_BEING_CALLED__,由于这个没有响应的 aspects ,其实会直接跳到原来的处理逻辑,并不会有其他附加影响。
static void aspect_deregisterTrackedSelector(id self, SEL selector) {
if (!class_isMetaClass(object_getClass(self))) return;
NSMutableDictionary *swizzledClassesDict = aspect_getSwizzledClassesDict();
NSString *selectorName = NSStringFromSelector(selector);
Class currentClass = [self class];
AspectTracker *subclassTracker = nil;
do {
AspectTracker *tracker = swizzledClassesDict[currentClass];
if (subclassTracker) {
[tracker removeSubclassTracker:subclassTracker hookingSelectorName:selectorName];
} else {
[tracker.selectorNames removeObject:selectorName];
}
if (tracker.selectorNames.count == 0 && tracker.selectorNamesToSubclassTrackers) {
[swizzledClassesDict removeObjectForKey:currentClass];
}
subclassTracker = tracker;
}while ((currentClass = class_getSuperclass(currentClass)));
}
还要移除AspectTracker里面所有标记的swizzledClassesDict。销毁全部记录的selector。
AspectsContainer *container = aspect_getContainerForObject(self, selector);
if (!container.hasAspects) {
// Destroy the container
aspect_destroyContainerForObject(self, selector);
// Figure out how the class was modified to undo the changes.
NSString *className = NSStringFromClass(klass);
if ([className hasSuffix:AspectsSubclassSuffix]) {
Class originalClass = NSClassFromString([className stringByReplacingOccurrencesOfString:AspectsSubclassSuffix withString:@""]);
NSCAssert(originalClass != nil, @"Original class must exist");
object_setClass(self, originalClass);
AspectLog(@"Aspects: %@ has been restored.", NSStringFromClass(originalClass));
// We can only dispose the class pair if we can ensure that no instances exist using our subclass.
// Since we don't globally track this, we can't ensure this - but there's also not much overhead in keeping it around.
//objc_disposeClassPair(object.class);
}else {
// Class is most likely swizzled in place. Undo that.
if (isMetaClass) {
aspect_undoSwizzleClassInPlace((Class)self);
}else if (self.class != klass) {
aspect_undoSwizzleClassInPlace(klass);
}
}
}
最后,我们还需要还原类的AssociatedObject关联对象,以及用到的AspectsContainer容器。
static void aspect_destroyContainerForObject(id<NSObject> self, SEL selector) {
NSCParameterAssert(self);
SEL aliasSelector = aspect_aliasForSelector(selector);
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, aliasSelector, nil, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN);
}
这个方法销毁了AspectsContainer容器,并且把关联对象也置成了nil。
static void aspect_undoSwizzleClassInPlace(Class klass) {
NSCParameterAssert(klass);
NSString *className = NSStringFromClass(klass);
_aspect_modifySwizzledClasses(^(NSMutableSet *swizzledClasses) {
if ([swizzledClasses containsObject:className]) {
aspect_undoSwizzleForwardInvocation(klass);
[swizzledClasses removeObject:className];
}
});
}
aspect_undoSwizzleClassInPlace会再调用aspect_undoSwizzleForwardInvocation方法。
static void aspect_undoSwizzleForwardInvocation(Class klass) {
NSCParameterAssert(klass);
Method originalMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(klass, NSSelectorFromString(AspectsForwardInvocationSelectorName));
Method objectMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(NSObject.class, @selector(forwardInvocation:));
// There is no class_removeMethod, so the best we can do is to retore the original implementation, or use a dummy.
IMP originalImplementation = method_getImplementation(originalMethod ?: objectMethod);
class_replaceMethod(klass, @selector(forwardInvocation:), originalImplementation, "v@:@");
AspectLog(@"Aspects: %@ has been restored.", NSStringFromClass(klass));
}
最后还原ForwardInvocation的Swizzling,把原来的ForwardInvocation再交换回来。
六. 关于Aspects 的一些 “坑”

在Aspects这个库了,用到了Method Swizzling有几处,这几处如果处理不好,就会掉“坑”里了。
1.aspect_prepareClassAndHookSelector 中可能遇到的“坑”
在aspect_prepareClassAndHookSelector方法中,会把原始的selector hook成_objc_msgForward。但是如果这里的selector就是_objc_msgForward会发生什么呢?
其实这里的坑在作者的代码注释里面已经隐藏的提到了。
在__ASPECTS_ARE_BEING_CALLED__方法中,最后转发消息的那段代码里面有这样一段注释
// If no hooks are installed, call original implementation (usually to throw an exception)
看到这段注释以后,你肯定会思考,为何到了这里就会throw an exception呢?原因是因为找不到NSSelectorFromString(AspectsForwardInvocationSelectorName)对应的IMP。
再往上找,就可以找到原因了。在实现aspect_prepareClassAndHookSelector中,会判断当前的selector是不是_objc_msgForward,如果不是msgForward,接下来什么也不会做。那么aliasSelector是没有对应的实现的。
由于 forwardInvocation 被 aspects 所 hook ,最终会进入到 aspects 的处理逻辑__ASPECTS_ARE_BEING_CALLED__中来,此时如果没有找不到 aliasSelector 的 IMP 实现,因此会在此进行消息转发。而且子类并没有实现 NSSelectorFromString(AspectsForwardInvocationSelectorName),于是转发就会抛出异常。
这里的“坑”就在于,hook的selector如果变成了_objc_msgForward,就会出现异常了,但是一般我们不会去hook _objc_msgForward这个方法,出现这个问题的原因是有其他的Swizzling会去hook这个方法。
比如说JSPatch把传入的 selector 先被 JSPatch hook ,那么,这里我们将不会再处理,也就不会生成 aliasSelector 。就会出现闪退的异常了。
static Class aspect_hookClass(NSObject *self, NSError **error) {
...
subclass = objc_allocateClassPair(baseClass, subclassName, 0);
...
IMP originalImplementation = class_replaceMethod(subclass, @selector(forwardInvocation:), (IMP)__ASPECTS_ARE_BEING_CALLED__, "v@:@");
if (originalImplementation) {
class_addMethod(subclass, NSSelectorFromString(AspectsForwardInvocationSelectorName), originalImplementation, "v@:@");
} else {
Method baseTargetMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(baseClass, @selector(forwardInvocation:));
IMP baseTargetMethodIMP = method_getImplementation(baseTargetMethod);
if (baseTargetMethodIMP) {
class_addMethod(subclass, NSSelectorFromString(AspectsForwardInvocationSelectorName), baseTargetMethodIMP, "v@:@");
}
}
...
}
这里在这篇文章中给出了一个解决办法:
在对子类的 forwardInvocation方法进行交换而不仅仅是替换,实现逻辑如下,强制生成一个 NSSelectorFromString(AspectsForwardInvocationSelectorName)指向原对象的 forwardInvocation的实现。
注意如果 originalImplementation为空,那么生成的 NSSelectorFromString(AspectsForwardInvocationSelectorName) 将指向 baseClass 也就是真正的这个对象的 forwradInvocation ,这个其实也就是 JSPatch hook 的方法。同时为了保证 block 的执行顺序(也就是前面介绍的 before hooks / instead hooks / after hooks ),这里需要将这段代码提前到 after hooks 执行之前进行。这样就解决了 forwardInvocation 在外面已经被 hook 之后的冲突问题。
谢谢简书的大神 @zhao0 指点,这篇文章详细分析了Aspect和JSPatch各种兼容性问题,经过详细的分析,最后只有4种不兼容的情况。
2. aspect_hookSelector 可能出现的 “坑”
在Aspects中主要是hook selector,此时如果有多个地方会和Aspects去hook相同方法,那么也会出现doesNotRecognizeSelector的问题。
举个例子,比如说在NSArray中用Aspects 去hook了objectAtIndex的方法,然后在NSMutableArray中Swizzling了objectAtIndex方法。在 NSMutableArray中,调用objectAtIndex就有可能出错。
因为还是在于Aspects hook 了selector之后,会把原来的selector变成_objc_msgForward。等到NSMutableArray再去hook这个方法的时候,记录的是IMP就是_objc_msgForward这个了。如果这时objc_msgSend执行原有实现,就会出错了。因为原有实现已经被替换为_objc_msgForward,而真的IMP由于被Aspects先Swizzling掉了,所以找不到。
解决办法还是类似JSPatch的解决办法:
把-forwardInvocation:也进行Swizzling,在自己的-forwardInvocation:方法中进行同样的操作,就是判断传入的NSInvocation的Selector,被Swizzling的方法指向了_objc_msgForward(或_objc_msgForward_stret)如果是自己可以识别的Selector,那么就将Selector变为原有Selector在执行,如果不识别,就直接转发。
最后
最后用一张图总结一下Aspects整体流程:
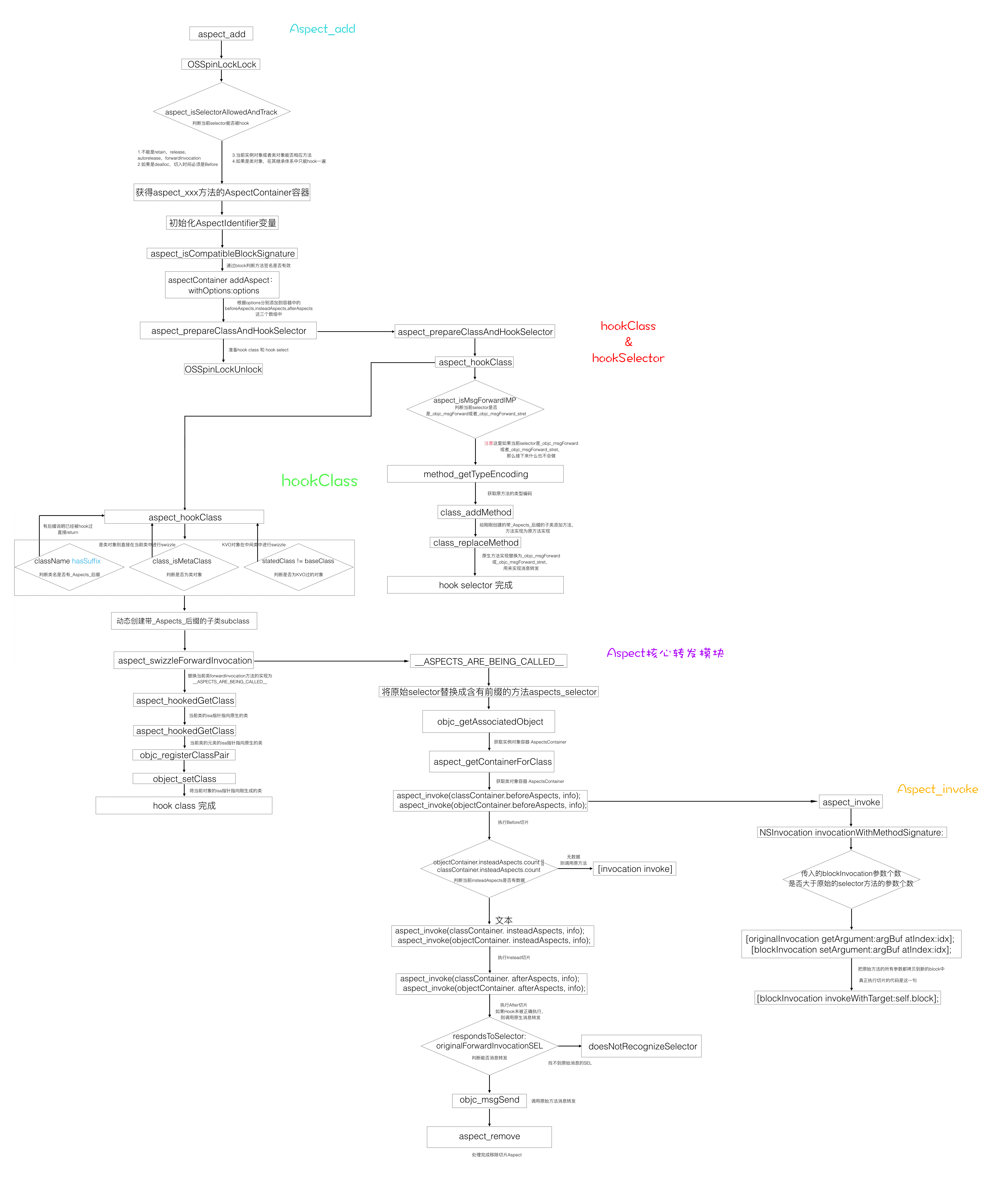
请大家多多指教。
